Psychometric evaluation of EQ-5D-5L in OHCA survivors from the TTM2 trial: a post hoc analysis
- PMID: 40530409
- PMCID: PMC12173684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resplu.2025.100994
Psychometric evaluation of EQ-5D-5L in OHCA survivors from the TTM2 trial: a post hoc analysis
Abstract
Aims: Our aim was to investigate the psychometric properties of the health assessment instrument EQ-5D-5L in OHCA survivors.
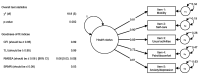
Methods: We included survivors from the Targeted Hypothermia versus Targeted Normothermia after OHCA (TTM2) trial, who completed EQ-5D-5L at 6 months. Confirmatory factor analysis was used to evaluate the hypothesised unidimensional latent structure of EQ level sum score (EQ LSS), summarizing scores across Mobility, Self-care, Usual activities, Pain/discomfort, and Anxiety/depression. Differential item functioning was evaluated for age. We examined internal consistency and precision for the EQ LSS. We evaluated construct validity of EQ LSS, EQ value and EQ VAS, using the modified Rankin Scale and Montreal Cognitive Assessment, representing functional outcome and cognitive function-two common health challenges experienced by OHCA survivors.
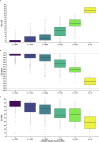
Results: 783 of 939 (84%) eligible survivors were included. Confirmatory factor analysis showed good model fit and strong factor loadings for all dimensions (0.61-0.90). We observed a significant but negligible effect of age on Mobility (β = 0.29, p < 0.001, ΔR2 = 0.019). Internal consistency was 0.88. The floor effect was 35%. Survivors with more functional dependency and/or cognitive problems reported significantly worse health by EQ LSS, EQ value, and EQ VAS (all, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The psychometric properties of EQ LSS support its use to measure health status in OHCA research. The strong association between health and functional dependency indicate robust and comparable construct validity for EQ LSS, EQ value, and EQ VAS in this sample.
Keywords: Cross-sectional studies; Health status; Heart arrest; Patient reported outcome measures; Psychometrics; Validation study.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: The co-author Tobias Cronberg serves as a member of the editorial board of the Resuscitation journal. All other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Haywood K., Whitehead L., Nadkarni V.M., et al. COSCA (Core Outcome Set for Cardiac Arrest) in adults: an Advisory statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2018;127:147–163. - PubMed
-
- Sawyer K.N., Camp-Rogers T.R., Kotini-Shah P., et al. Sudden cardiac arrest survivorship: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e654–e685. - PubMed
-
- Parkin D., Rice N., Devlin N. Statistical analysis of EQ-5D profiles: does the use of value sets bias inference? Med Decis Making. 2010;30:556–565. - PubMed
-
- Devlin N., Parkin D., Janssen B. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. Methods for Analysing and Reporting EQ-5D Data. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

