Long-Term Detection of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation in Cryptogenic Stroke Patients With Insertable Cardiac Monitors
- PMID: 40530496
- PMCID: PMC12174957
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.70251
Long-Term Detection of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation in Cryptogenic Stroke Patients With Insertable Cardiac Monitors
Abstract
Background: Long-term continuous monitoring with insertable cardiac monitor (ICM) is recommended after cryptogenic stroke (CS) by current guidelines to detect subclinical atrial fibrillation (SCAF). However, long-term real-world data on ICM-SCAF detection and ensuing therapy are limited. The aim of this study was to assess long-term SCAF detection rate in a large cohort of CS patients with ICM.
Methods: Data of consecutive CS patients receiving ICM from September 2016 to February 2024 in 20 Italian centers were collected. Patients were followed with remote and outpatient follow-up according to clinical practice. SCAF was diagnosed if a device-detected SCAF daily burden ≥ 5 min was confirmed by a cardiologist.
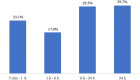
Results: Seven hundred and eighty-nine CS patients with ICM (mean age 69.3 ± 11.7 years, 40.3% females, 79.0% CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 4) were monitored for a mean of 27.3 (IQR:14.2-42.5) months after index stroke. SCAF was diagnosed in 229 (29.0%) patients, with a cumulative detection rate of 37.0% (IQR: 32.9%-41.5%) 48 months after the stroke, and was asymptomatic in 198 (86.5%). Sixty-eight (29.7%) patients had one or more days with a 24-h SCAF burden. Median time from index stroke to SCAF diagnosis was 6.9 (IQR: 2.1-17.0) months. After SCAF diagnosis, anticoagulants were prescribed to 210 (95.9%) patients out of 219 not already assuming them at baseline. CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 5, anterior circulation stroke, and cortical lesions were independent predictors of SCAF diagnosis.
Conclusions: This multicenter real-world project confirmed that ICM allows the detection of SCAF in one third of CS patients 48 months after the stroke, leading to anticoagulation in most of them.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cardiac remote monitoring; cryptogenic stroke; insertable cardiac monitor; stroke.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
L.P. serves on the editorial board of Neurology, Cerebrovascular Diseases, European Stroke Journal, Cerebral Circulation Cognition and Behavior, and is associate editor of Neurological Sciences. He has received consultation fees from PIAM, Medtronic, and Amicus. G.M. received modest consultancy fees and speaker's fees from Medtronic and Boston Scientific. A.U. received modest consultancy fees and speaker's fees from Medtronic. No other declare conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brachmann J., Morillo C. A., Sanna T., et al., “Uncovering Atrial Fibrillation Beyond Short‐Term Monitoring in Cryptogenic Stroke Patients: Three‐Year Results From the Cryptogenic Stroke and Underlying Atrial Fibrillation Trial,” Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology 9, no. 1 (2016): e003333, 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003333. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsivgoulis G., Triantafyllou S., Palaiodimou L., et al., “Prolonged Cardiac Monitoring and Stroke Recurrence: A Meta‐Analysis,” Neurology 98 (2022): e1942–e1952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

