Knockdown of miR-204-5p promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via the Wnt2/Ephrin-A2/EphA7 pathway
- PMID: 40530558
- PMCID: PMC12188836
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002184
Knockdown of miR-204-5p promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via the Wnt2/Ephrin-A2/EphA7 pathway
Abstract
Objective: Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) can cause short- and long-term neurological damage. MicroRNA (miR)-204-5p is closely associated with nerve injury caused by brain injury, but its mechanism in HIBD is not very clear.
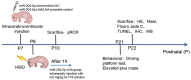
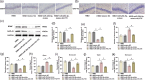
Methods: The neonatal rat's HIBD model was constructed by the modified Rice-Vannucci method, and the expression of miR-204-5p was detected. After overexpression or knockdown of miR-204-5p and application of Wnt2 activator HLY78, the histopathological changes and neuronal degeneration in the hippocampal CA1 region were observed with pathological staining. The neurological function was assessed with a diving platform test and elevated plus-maze test. Nerve regeneration-related protein and Wnt2/Ephrin-A2 (Eph receptor-interacting proteins)/EphA7 (erythropoi-etin-producing hepatomocellular receptor) signaling pathway protein levels were detected by immunohistochemistry and western blot, respectively.
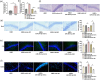
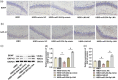
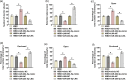
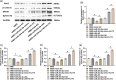
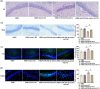
Results: miR-204-5p was highly expressed in HIBD. When miR-204-5p was knocked down, the morphology of nerve cells and Nissl bodies was notably improved, Fluoro-Jade C and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling-positive cells number was significantly reduced. The levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and growth-associated protein 43 were significantly increased, and the behavioral indicators of the diving platform and elevated plus-maze test were significantly alleviated. The nerve injury was repaired, and the Wnt2/Ephrin-A2/EphA7 signaling pathway protein was notably elevated. The overexpressed miR-204-5p aggravated the nerve injury in HIBD rats. After the application of HLY78, the neuropathological damage of HIBD rats was further repaired, and the nerve regeneration and function were also significantly improved.
Conclusion: Knockdown of miR-204-5p can improve HIBD in neonatal rats by activating the Wnt2/Ephrin-A2/EphA7 signaling pathway to encourage nerve regeneration and functional recovery.
Keywords: HIBD; Wnt2/Ephrin-A2/EphA7 pathway; miR-204-5p; nerve regeneration.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Greco P, Nencini G, Piva I, Scioscia M, Volta CA, Spadaro S, et al. Pathophysiology of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future. Acta Neurol Belg 2020; 120:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Gou Z, Su X, Hu X, Zhou Y, Huang L, Fan Y, et al. Melatonin improves hypoxic-ischemic brain damage through the Akt/Nrf2/Gpx4 signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull 2020; 163:40–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

