Betaine protects cerebral microvascular endothelium and ameliorates hypertension-induced cognitive dysfunction via upregulation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase/nitric monoxide signaling pathway
- PMID: 40530574
- PMCID: PMC12337935
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000004085
Betaine protects cerebral microvascular endothelium and ameliorates hypertension-induced cognitive dysfunction via upregulation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase/nitric monoxide signaling pathway
Abstract
Objectives: Hypertension-induced endothelial damage in cerebral microvessels is a key factor contributing to vascular cognitive impairment (VCI). Endothelial function stabilization considerably depends on the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)/nitrogen monoxide (NO) pathway. Furthermore, the eNOS/NO signaling pathway plays a role in stabilizing the vascular endothelium. Although betaine (bet) has been shown to improve cognitive dysfunction, its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to determine whether betaine protects cognitive function by regulating eNOS/NO activity.
Methods: Male 7-month-old spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were randomly assigned to four groups: SHR, Bet, Bet and N(G)-Nitroarginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME), and L-NAME groups. Male 7-month-old Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY) served as controls. All animals received treatment or saline for 4 weeks. In-vitro experiments were conducted using rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (RBMECs) treated with either homocysteine (Hcy) or betaine. Behavioral experiments, western blotting, pathological tissue staining, Doppler ultrasound technique, and ELISA were employed to assess the impact of hypertension on cognitive and endothelial functions.
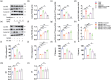
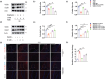
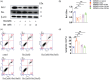
Results: Hypertension led to cognitive decline in SHR by causing endothelial dysfunction, blood-brain barrier disruption, inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Bet administration significantly improved these pathological indicators of cognitive impairment; however, the eNOS inhibitor L-NAME reversed its effects.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that betaine protects vascular endothelium and improves VCI by modulating the eNOS/NO signaling pathway.
Keywords: betaine; endothelial dysfunction; endothelial nitric oxide synthase; hypertension; vascular cognitive impairment.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Li C, Zhu Y, Ma Y, Hua R, Zhong B, Xie W. Association of cumulative blood pressure with cognitive decline, dementia, and mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol 2022; 79:1321–1335. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

