IRE1α RNase activity is critical for early embryo development by degrading maternal transcripts
- PMID: 40530690
- PMCID: PMC12203788
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf520
IRE1α RNase activity is critical for early embryo development by degrading maternal transcripts
Abstract
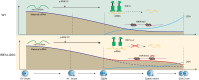
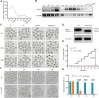
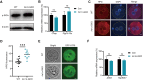
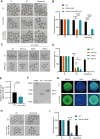
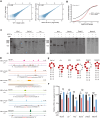
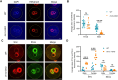
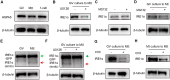
During maternal-to-zygotic transition, oocytes and embryos undergo massive maternal mRNA degradation. Three key events are related to RNA degradation: oocyte meiotic resumption, fertilization, and zygotic genome activation (ZGA). In this study, we unexpectedly discover that the UPR (unfolded protein response) protein IRE1α is critical for post-fertilization maternal messenger mRNA (mRNA) degradation. IRE1α is specifically expressed from the metaphase II oocytes to four-cell embryos, with its translation dependent on the ERK1/2 pathway. Oocyte-specific deletion of the IRE1α RNase domain resulted in female infertility, characterized by embryonic developmental arrest at the one-cell or two-cell stage, and failure to degrade maternal mRNAs destined for elimination. Using IRE1α-Flag knock-in mouse model and LACE-seq, as well as in vitro analysis, we show that IRE1α can directly bind and cleave maternal mRNAs after fertilization. Moreover, IRE1α-mediated mRNA decay is essential for ZGA and histone modifications. This study unveils an important function of IRE1α in early embryonic development through regulated IRE1α-dependent decay, independent of the canonical IRE1α-XBP1 signaling pathway, thereby revealing a novel molecular mechanism underlying maternal mRNA degradation triggered by fertilization.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32230028/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32471171/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32200664/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023B1515120027/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2023A1515010496/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

