Genomic and machine learning approaches to predict antimicrobial resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- PMID: 40530807
- PMCID: PMC12323353
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02632-24
Genomic and machine learning approaches to predict antimicrobial resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Abstract
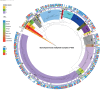
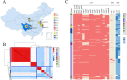
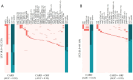
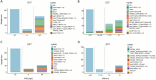
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a multidrug-resistant pathogen, which poses a major challenge to clinical management due to its increasing resistance to common antibiotics, such as levofloxacin (LEV) and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), and poor clinical response to treatment. There is an urgent need for rapid and reliable antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) methods to improve treatment outcomes. This study collected 441 S. maltophilia strains, performed whole-genome sequencing, and used machine learning to identify key resistance determinants for LEV and SXT, constructing predictive models for resistance phenotypes. The 441 S. maltophilia strains we collected show significant genomic diversity and representative lineage distribution. Machine learning identified key resistance markers for LEV and SXT, improving area under the curve values to 92.80% for LEV and 95.44% for SXT. Validation accuracies reached 94.87% for LEV and 96.27% for SXT. Mutations in parC, smeT, and gyrA were strongly associated with LEV resistance. The gene presence of sul1, sul2, and CEQ03_18740, as well as gene mutations in Gsh2, prmA, and gspD, were highly correlated with SXT resistance. These findings suggest that integrating genome-based markers can enhance the prediction of antimicrobial resistance, offering a robust method for clinical application. Genotypic AST can reliably predict resistance phenotypes, providing a promising alternative to traditional AST methods for S. maltophilia infections.
Importance: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is an emerging multidrug-resistant pathogen, making treatment challenging and requiring more effective diagnostic methods. This study offers a novel approach by integrating whole-genome sequencing with machine learning to identify key resistance markers for levofloxacin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The predictive models developed can reliably forecast antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, providing a faster and more accurate alternative to traditional susceptibility testing. This approach not only enhances clinical decision-making but also aids in the timely administration of appropriate therapies. By identifying specific genomic markers associated with resistance, this study lays the foundation for future development of personalized treatment strategies, addressing the growing concern of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; antimicrobial resistance prediction; machine learning; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retrospective analysis of antibiotic resistance profiles and frequency of resistance genes in clinical Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2025 May 22;72(2):139-144. doi: 10.1556/030.2025.02582. Print 2025 Jun 20. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2025. PMID: 40402576
-
Rapid prediction of antibiotic resistance in Enterobacter cloacae complex using whole-genome and metagenomic sequencing.mSystems. 2025 Jul 22;10(7):e0058425. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00584-25. Epub 2025 Jun 12. mSystems. 2025. PMID: 40503893 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity of Stenotrophomonas spp. and Its Impact on Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Infections.Microb Drug Resist. 2025 Aug;31(8):241-249. doi: 10.1177/10766294251359795. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Microb Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40654279
-
Efflux pump systems as key contributors to multidrug resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Physiological roles and gene regulation.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2025 May 22;72(2):81-92. doi: 10.1556/030.2025.02578. Print 2025 Jun 20. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2025. PMID: 40402604 Review.
-
Therapeutic options for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections beyond co-trimoxazole: a systematic review.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008 Nov;62(5):889-94. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn301. Epub 2008 Jul 28. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18662945
References
-
- Sader HS, Farrell DJ, Flamm RK, Jones RN. 2014. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Gram-negative organisms isolated from patients hospitalised with pneumonia in US and European hospitals: results from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, 2009-2012. Int J Antimicrob Agents 43:328–334. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.01.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mendes ET, Paez JIG, Ferraz JR, Marchi AP, Silva I, Batista MV, Lima A de, Rossi F, Levin AS, Costa SF. 2020. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of patients colonized or infected by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: is resistance to sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim a problem? Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 62:e96. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202062096 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

