UNC0638 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry by blocking cathepsin L maturation
- PMID: 40530850
- PMCID: PMC12282183
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00741-25
UNC0638 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry by blocking cathepsin L maturation
Abstract
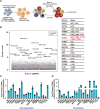
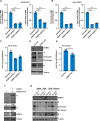
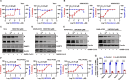
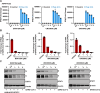
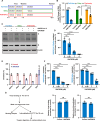
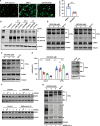
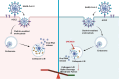
Since the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2, viral mutations have posed significant challenges in identifying therapeutic targets and developing broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. Post-translational modifications of genes involved in interferon production and signaling pathways play a crucial role in regulating interferon responses. In this study, we employed CRISPR-Cas9 screening based on adenine base editors to investigate functional amino acids in 1,278 innate immune-related genes. This approach, which converts A-T base pairs into G-C base pairs to probe the functional importance of specific amino acids, allowed us to identify 17 vital factors involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Among the candidate genes, genetic knockdown of EHMT2 exhibited the strongest antiviral effect. Further analysis revealed that UNC0638, a selective inhibitor of EHMT2, significantly reduced the endosomal entry of SARS-CoV-2 in pseudovirus assays. The observed inhibitory effect was consistently observed across multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Omicron. Mechanistically, UNC0638 reduced mature cathepsin L (CTSL) levels, impairing the proteolytic cleavage of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and subsequent membrane fusion, a critical step for viral entry. Our findings uncover EHMT2 as a host dependency factor and reveal the antiviral mechanism of EHMT2 inhibitors through CTSL maturation blockade. These results advance the understanding of host factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection and provide a strategic framework for developing host-targeted antiviral therapies.IMPORTANCEIn this study, we demonstrated that knockdown or knockout of EHMT2 inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection, and inhibitors of EHMT2, including UNC0638, UNC0642, and BIX01294 showed similar restrictive effects. Mechanistically, the EHMT2 inhibitor UNC0638 restricts spike-mediated cell entry by inhibiting the maturation of CTSL, a critical protease required for SARS-CoV-2 entry via the endosomal pathway. Importantly, CTSL is not only essential for SARS-CoV-2 but also plays a key role in the entry of other coronaviruses that utilize similar pathways. Therefore, EHMT2 inhibitors could have broader applications as pan-coronavirus therapeutic agents.
Keywords: EHMT2; SARS-CoV-2; UNC0638; cathepsin L; viral entry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guery B, Poissy J, el Mansouf L, Séjourné C, Ettahar N, Lemaire X, Vuotto F, Goffard A, Behillil S, Enouf V, Caro V, Mailles A, Che D, Manuguerra J-C, Mathieu D, Fontanet A, van der Werf S, MERS-CoV study group . 2013. Clinical features and viral diagnosis of two cases of infection with middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus: a report of nosocomial transmission. Lancet 381:2265–2272. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60982-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

