Oral delivery of GLP-1 peptide using recombinant Lactobacillus gasseri for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40530879
- PMCID: PMC12323307
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02828-24
Oral delivery of GLP-1 peptide using recombinant Lactobacillus gasseri for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
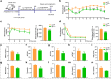
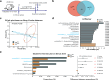
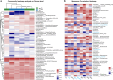
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an effective therapeutic peptide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Here, we constructed an effective probiotic-based oral GLP-1 delivery system by engineering the probiotic strain of Lactobacillus gasseri (LgsGPA) to secrete GLP-1 fusion peptide, which combines GLP-1 with protein transduction domain (PTD) and a serum albumin binding peptide (ABP), GLP-1-PTD-ABP (GPA). The supernatants of LgsGPA cultures significantly upregulated the expression of PDX-1 and stimulated insulin release in Min6 cells. Daily oral administration of LgsGPA in db/db mice significantly alleviated insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia. Simultaneously, the abundance of unclassified_f_Erysipelotrichaceae and Intestinimonas was significantly reduced in db/db mice, while the average abundance of Akkermansia increased in the SD rats. These findings demonstrate that the probiotic-based delivery system represents a versatile and effective strategy for the oral administration of therapeutic peptides. Collectively, our results highlight the potential of this probiotic-based approach as a promising therapeutic and preventive intervention for T2DM.IMPORTANCEIt is important to develop the oral delivery strategy for therapeutic peptides. Due to issues with patient adherence and the low oral bioavailability of current administration methods, researchers have been exploring oral delivery strategies for GLP-1 analogs for many years, including the use of advanced microbiome therapeutics (AMTs). AMTs offer the potential to use engineered microbes for innovative therapeutic applications, such as the oral delivery of GLP-1 analogs. Our approaches offer a general oral delivery strategy for therapeutic peptides. The probiotic-based approach represents a promising method for treating and preventing T2DM.
Keywords: GLP-1 analog; Lactobacillus gasseri; advanced microbiome delivery; glucagon-like peptide-1; gut microbiota; oral delivery; protein transduction domain; serum albumin binding peptide; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.Eur J Endocrinol. 2025 Jun 30;193(1):G1-G48. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvaf116. Eur J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40652450
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Mazdutide, a dual agonist targeting GLP-1R and GCGR, mitigates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction: mechanistic insights from multi-omics analysis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jul;117:105791. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105791. Epub 2025 Jun 6. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40479843 Free PMC article.
-
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Glu-07: A Promising Probiotic Candidate for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Jul 22;82(9):402. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04391-y. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40694135 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for people with chronic kidney disease and diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 18;2(2):CD015849. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015849.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39963952
References
-
- Divakaran S, Singh A, Biery D, Yang J, DeFilippis EM, Collins BL, Ramsis M, Qamar A, Hainer J, Klein J, Cannon CP, Polk DM, Plutzky J, Nasir K, Januzzi JL, Di Carli MF, Bhatt DL, Blankstein R. 2020. Diabetes is associated with worse long-term outcomes in young adults after myocardial infarction: the partners YOUNG-MI registry. Diabetes Care 43:1843–1850. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0998 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furtado RHM, Bonaca MP, Raz I, Zelniker TA, Mosenzon O, Cahn A, Kuder J, Murphy SA, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JPH, Ruff CT, Nicolau JC, Gause-Nilsson IAM, Fredriksson M, Langkilde AM, Sabatine MS, Wiviott SD. 2019. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and previous myocardial infarction. Circulation 139:2516–2527. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.039996 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patel KV, Budoff MJ, Valero-Elizondo J, Lahan S, Ali SS, Taha MB, Blaha MJ, Blankstein R, Shapiro MD, Pandey A, Arias L, Feldman T, Cury RC, Cainzos-Achirica M, Shah SH, Ziffer JA, Fialkow J, Nasir K. 2023. Coronary atherosclerosis across the glycemic spectrum among asymptomatic adults: the Miami Heart Study at Baptist Health South Florida. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 16:e015314. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.123.015314 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cong Z, Zhou Q, Li Y, Chen LN, Zhang ZC, Liang A, Liu Q, Wu X, Dai A, Xia T, Wu W, Zhang Y, Yang D, Wang MW. 2022. Structural basis of peptidomimetic agonism revealed by small- molecule GLP-1R agonists Boc5 and WB4-24. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119:e2200155119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200155119 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

