Detection of Mucorales antigen in bronchoalveolar lavage samples using a newly developed lateral-flow device
- PMID: 40530880
- PMCID: PMC12239717
- DOI: 10.1128/jcm.00226-25
Detection of Mucorales antigen in bronchoalveolar lavage samples using a newly developed lateral-flow device
Abstract
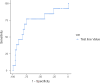
A murine IgG2b monoclonal antibody, named TG11, binding to an extracellular polysaccharide antigen secreted by all Mucorales fungi has been recently developed and integrated into a lateral-flow device (TG11-LFD). The aim of this study was to establish the clinical performance of TG11-LFD on bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids for the diagnosis of mucormycosis. Thirteen BAL samples from 13 patients with mucormycosis, all of which tested positive for Mucorales qPCR (Mucor/Rhizopus [n = 5], Lichtheimia [n = 2], Rhizomucor [n = 5], and Cunninghamella [n = 1]), were used to assess the TG11-LFD. We also selected 49 BAL samples from 25 patients with other invasive fungal infections (IFI) (aspergillosis, Pneumocystis infection, candidiasis, and possible IFI) and from 20 patients without IFI for use as negative controls. The intensities of the test and control lines were recorded using a Cube reader. The diagnostic performance was assessed by analyzing the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve with the Jamovi software package (version 2.6.13). The area under the curve of the ROC curve was 0.739. Using a threshold value positivity ≤531 artificial units, the TG11-LFD test has a sensitivity and specificity of 76.92% and 75.51%, respectively, a positive predictive value of 45.45%, and a negative predictive value of 92.5%. In this study, we evaluated the performance of TG11-LFD on clinical samples for the first time and demonstrated its significant potential for enhancing the rapid detection of mucormycosis. Combining antigen detection with qPCR, as successfully applied in the diagnosis of aspergillosis, is likely to yield the most reliable diagnostic approach.IMPORTANCEMucormycosis is a severe emerging, invasive fungal disease caused by fungi in the order Mucorales. The mortality rate remains high at approximately 50%. Rapid diagnosis and prompt initiation of targeted treatment are associated with an improved prognosis. Gold standard diagnostic procedures have poor sensitivity and long turnaround times. Mucorales polymerase chain reaction in blood and respiratory samples has improved diagnosis, but this technique is not widely available due to high costs and the need for specialist equipment. A prototype lateral-flow device (TG11-LFD) incorporating a mouse monoclonal antibody, which binds to an extracellular polysaccharide antigen specific to Mucorales fungi, has been recently developed. In this study, we evaluated for the first time the performance of the TG11-LFD test on clinical bronchoalveolar lavage fluids for diagnosing mucormycosis. With 76.92% sensitivity and 75.51% specificity, this innovative, simple, and affordable approach shows great potential for improving the rapid diagnosis of mucormycosis.
Keywords: Mucorales; antigen detection; diagnosis; lateral flow device; mucormycosis.
Conflict of interest statement
L.M. and S.I. report personal travel grants from Gilead and Pfizer. A.D. reports personal travel grants from Pfizer. C.T. is Director of ISCA Diagnostics Limited.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utility of Mucorales polymerase chain reaction to diagnose Rhizomucor infections in neutropenic patients.Med Mycol. 2025 Jan 25;63(2):myaf013. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaf013. Med Mycol. 2025. PMID: 39909471
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

