Synergistic antibacterial activity and prevention of drug resistance of daptomycin combined with fosfomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 40530996
- PMCID: PMC12327001
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01609-24
Synergistic antibacterial activity and prevention of drug resistance of daptomycin combined with fosfomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
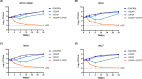
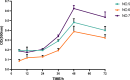
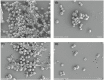
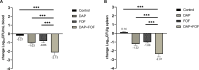
The combination of daptomycin and fosfomycin is attracting attention due to the rising resistance observed in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Most studies indicate that this combination exhibits synergistic or additive antimicrobial activity against MRSA. However, its capacity to prevent resistance remains uncertain. In this study, we first investigated the antibacterial effect of daptomycin and fosfomycin on MRSA, followed by predicting MRSA resistance under the influence of different drugs using a resistance mutation selection window. Subsequently, we conducted preliminary analyses of drug resistance gene mutations in resistance mutants through gene sequencing technology. Additionally, we established an in vitro biofilm infection model to explore the internal tolerance associated with phenotypic alterations in biofilms and assess the combination's ability to prevent drug resistance. Combination drug sensitivity experiments demonstrated that daptomycin and fosfomycin synergistically enhanced antimicrobial effects against the tested strains. This combination reduced the mutant prevention concentration of each drug and narrowed the selection window for drug-resistant mutations. Sequencing results indicated that specific resistance genes were mutated in the single-drug mutants, while no mutations were detected in the combination. Furthermore, the combination exhibited stronger inhibition and removal of biofilm compared to single agents. In conclusion, the daptomycin-fosfomycin combination displays a synergistic antibacterial effect against MRSA and shows enhanced capacity to prevent bacterial resistance, likely attributed to its ability to inhibit resistance gene mutations and exhibit superior anti-biofilm activity.
Keywords: antibiotics resistance; daptomycin; fosfomycin; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
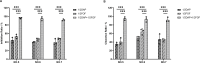

Similar articles
-
Synergistic activity of fosfomycin and flucloxacillin against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro and in vivo assessment.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2025 Jun 21;214(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s00430-025-00841-3. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40544222 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage infection drives loss of β-lactam resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Elife. 2025 Jul 10;13:RP102743. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102743. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40637714 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm potentials of vancomycin-loaded niosomal drug delivery system against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 8;24(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00874-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38978013 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic prophylaxis for the prevention of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) related complications in surgical patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 19;2013(8):CD010268. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010268.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23959704 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for the eradication of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 21;7(7):CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12:CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub5. PMID: 30030966 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

