Baseline Distress and Effectiveness of Survivor Video Narratives on Cancer-Associated Distress in Botswana: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 40532135
- PMCID: PMC12312413
- DOI: 10.1200/GO-24-00474
Baseline Distress and Effectiveness of Survivor Video Narratives on Cancer-Associated Distress in Botswana: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate baseline distress among patients with breast cancer in Botswana, and assess the impact of culturally tailored peer survivor video narratives on distress and its mediators.
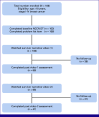
Methods: We enrolled patients with stage I-IV breast cancer at Princess Marina Hospital. A Setswana-translated National Comprehensive Cancer Network distress thermometer (DT) and problem list (PL) were used for distress screening. DT score of ≥4 was considered a positive screen for moderate to high (moderate-high) distress. We analyzed independent PL factors associated with moderate-high distress using logistic regression. Participants then watched one to two videos and completed a postintervention DT/PL assessment after each video at 4 and 8 weeks. We conducted descriptive statistics to explore the impact of the videos.
Results: One hundred six participants were enrolled, of whom 103 completed baseline DT and 106 completed baseline PL. Sixty-seven percent (69/103) of participants screened positive for moderate-high distress at baseline. Fear (odds ratio [OR], 11.25 [95% CI, 1.66 to 76.49]; P = .01) and appearance (OR, 4.96 [95% CI, 1.03 to 23.80]; P = .046) were PL factors significantly associated with moderate-high distress in the multivariable model. Sixty-eight and 47 participants completed postvideo assessments at approximately 4 and approximately 8 weeks, respectively. The greatest impact was observed at 8 weeks after watching two videos-29.8% of participants with moderate-high distress had no or mild distress. Similarly, there was a 29% (44%-15%; P = .005) and 17% (32%-15%; P = .03) absolute decrease from baseline to 8 weeks, in the proportion of patients who identified fear and appearance as sources of distress, respectively.
Conclusion: Two thirds of patients with breast cancer screened positive for moderate-high distress. Fear and appearance were sources of distress significantly associated with a positive screen. Our results show promising potential of peer survivor videos to mitigate distress and its potential mediators among patients with breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Hamilton J, Kruse H, Holcomb L, et al. : Distress and psychosocial needs: Demographic predictors of clinical distress after a diagnosis of cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs 22:390-397, 2018 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

