N6-methyladenosine-modified GPX2 impacts cancer cell stemness and TKI resistance through regulating of redox metabolism
- PMID: 40533443
- PMCID: PMC12177039
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07764-0
N6-methyladenosine-modified GPX2 impacts cancer cell stemness and TKI resistance through regulating of redox metabolism
Abstract
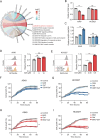
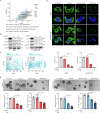
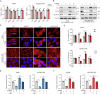
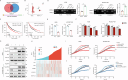
As a predominant oncogenic driver in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), EGFR frequently undergoes amplification or mutation, with EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) like gefitinib and erlotinib constituting frontline therapy for advanced EGFR-mutant cases. However, both primary and acquired resistance significantly limit clinical efficacy. Here, we revealed that glutathione metabolic pathway controlled by glutathione peroxidase GPX2 was abnormally activated in gefitinib-resistant A549 and HCC827-GR cell lines. Mechanistically, GPX2 triggers Hedgehog signaling activation through releasing GLI transcriptional regulator, promoting cancer stem cell (CSC) characteristics and TKI resistance. Notably, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on GPX2 mRNA mediated by METTL14 diminished its stability. In vivo, GPX2 deletion constrained glutathione metabolism and boosted the effectiveness of TKI in cell line-derived xenograft models. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that GPX2 serves as a positive regulator of both primary and acquired EGFR-TKI resistance and could be a promising therapeutic target for precise treatment of NSCLC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Tumor collection and analyses were conducted with the approval of the Committee on Ethics of Medicine of Naval Medical university. All patients gave written informed consent before participation in this study. Animal experiments were performed with approved ethics from the Animal Care and Use Committee of Fudan University (20160225-016). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Figures


References
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–54. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786–92. - PubMed
-
- Passaro A, Janne PA, Mok T, Peters S. Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat Cancer. 2021;2:377–91. - PubMed
-
- Tang ZH, Lu JJ. Osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. 2018;420:242–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

