Reversible proliferative arrest induced by rapid depletion of RNase MRP
- PMID: 40533478
- PMCID: PMC12177063
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60471-4
Reversible proliferative arrest induced by rapid depletion of RNase MRP
Abstract
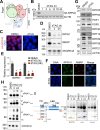
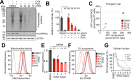
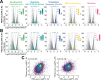
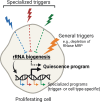
Cellular quiescence is a state of reversible proliferative arrest that plays essential roles in development, resistance to stress, aging, and longevity of organisms. Here we report that rapid depletion of RNase MRP, a deeply conserved RNA-based enzyme required for rRNA biosynthesis, induces a long-term yet reversible proliferative arrest in human cells. Severely compromised biogenesis of rRNAs along with acute transcriptional reprogramming precede a gradual decline of the critical cellular functions. Unexpectedly, many arresting cells show increased levels of histone mRNAs, which accumulate locally in the cytoplasm, and S-phase DNA amount. The ensuing proliferative arrest is entered from multiple stages of the cell cycle and can last for several weeks with uncompromised cell viability. Strikingly, restoring expression of RNase MRP leads to a complete reversal of the arrested state with resumed cell proliferation at the speed of control cells. We suggest that targeting rRNA biogenesis may provide a general strategy for rapid induction of a reversible proliferative arrest, with implications for understanding and manipulating cellular quiescence.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.M., W.F.M., and S.C. are inventors on a patent application filed by The Regents of the University of California (U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 63/581,832) describing the methods of inducing reversible proliferative arrest presented in the manuscript. J.M. and S.C. are the founders of StopTime Inc., a startup focused on identifying and developing methods and compounds for the induction of cell dormancy and hypometabolism. All authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

