Quality appraisal of radiomics-based studies on chondrosarcoma using METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS) and Radiomics Quality Score (RQS)
- PMID: 40533701
- PMCID: PMC12177113
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-025-02016-3
Quality appraisal of radiomics-based studies on chondrosarcoma using METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS) and Radiomics Quality Score (RQS)
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the methodological quality of radiomics-based studies on bone chondrosarcoma using METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS) and Radiomics Quality Score (RQS).
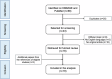
Methods: A literature search was conducted on EMBASE and PubMed databases for research papers published up to July 2024 and focused on radiomics in bone chondrosarcoma, with no restrictions regarding the study aim. Three readers independently evaluated the study quality using METRICS and RQS. Baseline study characteristics were extracted. Inter-reader reliability was calculated using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
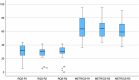
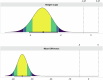
Results: Out of 68 identified papers, 18 were finally included in the analysis. Radiomics research was aimed at lesion classification (n = 15), outcome prediction (n = 2) or both (n = 1). Study design was retrospective in all papers. Most studies employed MRI (n = 12), CT (n = 3) or both (n = 1). METRICS and RQS adherence rates ranged between 37.3-94.8% and 2.8-44.4%, respectively. Excellent inter-reader reliability was found for both METRICS (ICC = 0.961) and RQS (ICC = 0.975). Among the limitations of the evaluated studies, the absence of prospective studies and deep learning-based analyses was highlighted, along with the limited adherence to radiomics guidelines, use of external testing datasets and open science data.
Conclusions: METRICS and RQS are reproducible quality assessment tools, with the former showing higher adherence rates in studies on chondrosarcoma. METRICS is better suited for assessing papers with retrospective design, which is often chosen in musculoskeletal oncology due to the low prevalence of bone sarcomas. Employing quality scoring systems should be promoted in radiomics-based studies to improve methodological quality and facilitate clinical translation.
Critical relevance statement: Employing reproducible quality scoring systems, especially METRICS (which shows higher adherence rates than RQS and is better suited for assessing retrospective investigations), is highly recommended to design radiomics-based studies on chondrosarcoma, improve methodological quality and facilitate clinical translation.
Key points: The low scientific and reporting quality of radiomics studies on chondrosarcoma is the main reason preventing clinical translation. Quality appraisal using METRICS and RQS showed 37.3-94.8% and 2.8-44.4% adherence rates, respectively. Room for improvement was noted in study design, deep learning methods, external testing and open science. Employing reproducible quality scoring systems is recommended to design radiomics studies on bone chondrosarcoma and facilitate clinical translation.
Keywords: Chondrosarcoma; Evidence-based radiology; Radiomics; Sarcoma; Texture analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not required for this study, which was based on a systematic review of the literature and did not include any new patients’ data. Consent for publication: Not required for this study, which was based on a systematic review of the literature and did not include any new patients’ data. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (2020) WHO classification of tumours: soft tissue and bone tumours. International Agency for Research on Cancer Press, Lyon

