Toxicity reduction in continuous, high productivity ethanol fermentation by Parageobacillus thermoglucosidasius using in situ microbubble gas stripping
- PMID: 40533748
- PMCID: PMC12177972
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-025-02754-5
Toxicity reduction in continuous, high productivity ethanol fermentation by Parageobacillus thermoglucosidasius using in situ microbubble gas stripping
Abstract
Ethanol concentrations above 4% (v/v) are required for economic bioethanol production due to the cost of recovery from dilute solutions. Although thermophilic bacteria have many potential advantages over Saccharomyces cerevisiae as process organisms for second generation bioethanol production, they are known to be less tolerant to ethanol, typically to concentrations less than 4% (v/v). To address this issue we have investigated the application of in situ gas-stripping of ethanol using microbubbles to increase the surface area per unit volume of gas, using fed-batch and continuous cultures of the engineered ethanologenic thermophile Parageobacillus thermoglucosidasius TM242. By using microbubbles generated at room temperature using a Desai-Zimmerman Fluid Oscillator, we initially operated a mixed batch and fed-batch fermentation, followed by a continuous fermentation and finally a chemostat fermentation, under conditions which would have generated in excess of 4% (v/v) ethanol. In all cases, gas stripping maintained the actual dissolved ethanol concentration below, or close to toxic levels. As the focus of this study was on demonstrating the efficiency of in situ microbubble gas stripping, to simplify the operation the latter two processes involved a combination of produced and supplemented ethanol, with the chemostat culture producing a nominal maximum 7.1% v/v based on glucose used (5.1-5.3% (v/v) based on ethanol recovered). This offers a practical way to produce second generation bio-ethanol from thermophiles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

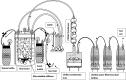
 = pump;
= pump;  = ice bath;
= ice bath;  = sterile filter;
= sterile filter;  = media flow;
= media flow;  = gas flow.
= gas flow.



References
-
- Hanaki K, Portugal-Pereira J. The effect of biofuel production on greenhouse gas emission reductions. In: Takeuchi K, Shiroyama H, Saito O, Matsuura M, editors. Biofuels and sustainability. Science for sustainable societies. Springer: Tokyo; 2018. p. 53–71. 10.1007/978-4-431-54895-9_6.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

