Aurora kinases signaling in cancer: from molecular perception to targeted therapies
- PMID: 40533769
- PMCID: PMC12175390
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02353-3
Aurora kinases signaling in cancer: from molecular perception to targeted therapies
Abstract
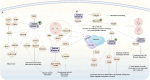
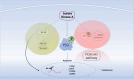
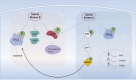
Aurora kinases, AURKA, AURKB, and AURKC, are serine/threonine kinases that play a vital role in regulating cell division and mitosis, particularly in the separation of chromosomes. These kinases are often overexpressed in human tumor cell lines, indicating their potential involvement in tumorigenesis. Preliminary evidence supports the use of Aurora kinase inhibitors for certain types of tumors, several AURKs inhibitors are currently under phase I and II trials. As a result, there is a growing interest in identifying small-molecule Aurora kinase inhibitors to develop as anti-cancer agents. The regulation of the cell cycle, including mitosis, is increasingly recognized as a key target in the fight against various forms of cancer. Novel drugs are being designed to inhibit the function of regulatory proteins, such as Aurora kinases, with the goal of creating personalized treatments. This review summarizes the biology of Aurora kinases in the context of cancer, integrating both preclinical and clinical data. It discusses the challenges and opportunities associated with using Aurora kinases to enhance cancer treatment. Future directions for Aurora kinase-based therapies include developing more selective inhibitors that minimize off-target effects and improve therapeutic efficacy. Researchers are also exploring combination therapies that use Aurora kinase inhibitors alongside other targeted treatments to overcome resistance and improve patient outcomes. Additionally, advancements in biomarker discovery are expected to facilitate the identification of patients most likely to benefit from Aurora kinase-targeted therapies, paving the way for more personalized approaches to cancer treatment.
Keywords: AKIs; AURKA; AURKB; AURKC; Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis; Targeted Therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

