Prospective analysis of B cell subset dynamics following telitacicept treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 40533865
- PMCID: PMC12175369
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03584-x
Prospective analysis of B cell subset dynamics following telitacicept treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease marked by B cell activation and autoantibody formation. Telitacicept, a dual inhibitor of the B cell pathway, neutralizes signals from B lymphocyte stimulator and a proliferation-inducing ligand. The aim of this study is to investigate the changes in detailed B cell subsets in SLE patients following Telitacicept treatment.
Methods: Twenty active SLE patients (SLEDAI-2 K ≥ 6) were enrolled, with B cell subsets analyses and clinical assessments conducted at 0, 4, 12, and 24 weeks after initiating Telitacicept treatment. Additionally, B cell subsets were measured in 21 healthy controls. Flow cytometry was used to quantify B cell subsets.
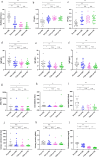
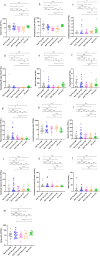
Results: After six months of treatment, a 95% (19/20) SRI-4 response rate and a 35% (7/20) achievement of LLDAS were recorded. Compared to baseline, there were significant reductions in SLEDAI-2 K scores and anti-dsDNA levels (both p < 0.001), along with increases in complement C3 and C4 levels (both p < 0.001). Additionally, there was a significant decrease in 24-h urine protein levels (p = 0.004). B cell subset analysis revealed decreases in total B cells (p < 0.05), transitional B cells, naive B cells, and short-lived plasma cells (all p < 0.01). The proportion of B regulatory (Breg) cell increased (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Combining telitacicept with standard therapy induced significant changes in B cell subsets and clinical markers in SLE patients. The reduction in naive and transitional B cells, along with the restoration of Breg cell, suggests a potential positive influence on immunoregulatory capacity.
Trial registration: Chineses Clinical Trials Registry; https://www.chictr.org.cn ; ChiCTR2400086874.
Keywords: B cell subsets; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Telitacicept.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee in Clinical Research of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (approval number KY2021-197). Informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to their inclusion in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Taubmann J, Müller F, Yalcin Mutlu M, Völkl S, Aigner M, Bozec A, Mackensen A, Grieshaber-Bouyer R, Schett G: CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Treatment: Unraveling the Role of B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis & rheumatology (Hoboken, NJ) 2024; 76(4):497-504. - PubMed
-
- Gómez-Urquiza JL, Romero-Bejar JL, Chami-Peña S, Suleiman-Martos N, Cañadas-De la Fuente GA, Molina E, Riquelme-Gallego B: Efficacy and Safety of New B Cell-Targeted Biologic Agent for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(14):4848. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

