The important role of chloroplasts in plant immunity
- PMID: 40534128
- PMCID: PMC12365846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2025.101420
The important role of chloroplasts in plant immunity
Abstract
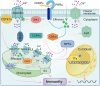
In nature, plants are under attack by a range of pathogens. To cope with these pathogens, plants have evolved a sophisticated immune system, including pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) initiated by pattern recognition receptors on the cell surface and effector-triggered immunity (ETI) activated by intracellular nucleotide-binding and leucine-rich repeat receptors. In recent years, increasing evidence has demonstrated that organelles such as the chloroplast play crucial roles in complete activation of plant immunity. In this review, we focus on the chloroplast and summarize its role in regulating the activation of immune events, including influx of calcium (Ca2+), accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), biosynthesis of phytohormones, and expression of defense-related genes. Because information exchange between the chloroplast and the nucleus is very important during plant immunity, we also highlight the importance of chloroplast-nucleus communication via stromules in plant immunity. This review reveals the function of the chloroplast in maintaining the trade-off between plant growth and immunity, and expands our understanding of how chloroplasts enable complete activation of plant immunity.
Keywords: Ca(2+); ROS; chloroplast; plant immunity; retrograde signals; stromule.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bi G., Zhou Z., Wang W., Li L., Rao S., Wu Y., Zhang X., Menke F.L.H., Chen S., Zhou J.M. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases directly link diverse pattern recognition receptors to the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2018;30:1543–1561. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00981. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

