Effectiveness of islatravir post-exposure prophylaxis after intravenous challenge with simian immunodeficiency virus in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 40534150
- PMCID: PMC12177105
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.26507
Effectiveness of islatravir post-exposure prophylaxis after intravenous challenge with simian immunodeficiency virus in rhesus macaques
Abstract
Introduction: Islatravir (ISL) is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) with robust antiretroviral activity. The efficacy of ISL administered for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) was evaluated in a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) rhesus macaque intravenous (IV) challenge model.
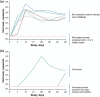
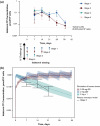
Methods: Twelve rhesus macaques were challenged with SIVmac251 via IV administration. After 24 hours, six animals received ISL 3.9 mg/kg (the minimum effective dose that gives maximal protection) and six animals were untreated controls. In stage 1, treated animals received 4 weekly oral doses of ISL and were monitored for SIV infection for 7 weeks after the last dose. In stage 2, uninfected, treated animals from stage 1 were challenged similarly; 24 hours after challenge, 3 weekly oral doses of ISL 3.9 mg/kg were initiated. The treated animals were monitored for 7 weeks, as in stage 1. Uninfected, treated animals (from stage 2) entered stage 3. In stage 3, the animals were challenged as in stage 2; 24 hours after challenge, 2 weekly oral doses of ISL 3.9 mg/kg were initiated. The treated animals were monitored for 7 weeks, as before. Finally, in stage 4, uninfected, treated animals were challenged using IV administration and 24 hours later were treated with a single oral dose of ISL 3.9 mg/kg and monitored for 7 weeks. Infection was monitored through plasma viral RNA and proviral DNA amplification. Virus-specific antibody responses were measured using a commercial assay. ISL concentrations in plasma and ISL triphosphate (ISL-TP) levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were measured longitudinally.
Results: All untreated controls were viraemic 7 days after SIVmac251 IV challenge. All six ISL-treated animals were completely protected in stages 1-3 (Fisher exact test p = 0.0022). In stage 4, two of six ISL-treated animals became infected with wild-type SIVmac251: viraemia was observed at days 14 and 49 in the two animals (Fisher exact test p = 0.06). Both animals had unquantifiable ISL-TP on the day viraemia was observed.
Conclusions: Two weekly oral doses of ISL 3.9 mg/kg, administered 24 hours post IV SIV exposure, prevents infection of rhesus macaques. These results support further investigation of a long-acting oral NRTTI for PEP.
Keywords: SIV; islatravir; islatravir‐TP; pharmacokinetic; post‐exposure prophylaxis; rhesus macaque.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Conflict of interest statement
KF, ND, DJH, JAG, MP, RV and TLD are current or former employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and may own stock and/or options in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. DJH is an inventor on related patents. MM, AG, LSB and BG have no conflicts to report.
Figures

References
-
- Hattori S, Ide K, Nakata H, Harada H, Suzu S, Ashida N, et al. Potent activity of a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, 4'‐ethynyl‐2‐fluoro‐2'‐deoxyadenosine, against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in a model using human peripheral blood mononuclear cell‐transplanted NOD/SCID Janus kinase 3 knockout mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(9):3887–3893. - PMC - PubMed
-
- CDC . Updated guidelines for antiretroviral postexposure prophylaxis after sexual, injection drug use, or other nonoccupational exposure to HIV‐United States. Centers for Disease Control; 2016. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Guidelines for HIV post‐exposure prophylaxis. 2024. Accessed March 4, 2025. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240095137. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

