Evaluation of the risk factors for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with choroidal detachment from the viewpoint of treatment patterns: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40534816
- PMCID: PMC12120457
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2025.06.13
Evaluation of the risk factors for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with choroidal detachment from the viewpoint of treatment patterns: a retrospective study
Abstract
Aim: To compare the proportion of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) associated with choroidal detachment (RRDCD) in the emergency surgery group with the routine inpatient surgery group and determine risk factors for RRDCD.
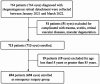
Methods: A total of 694 patients (694 eyes) diagnosed with RRD in the emergency surgery (the median duration of RRD was 5d) group were included from the Department of Ophthalmic Emergency, and 692 patients (eyes) in the routine inpatient surgery group (the median duration was 15d) were selected randomly from the Ocular Fundus Department. Demographics, refractive status, macular status, lens status, extent of retinal detachment, number of retinal breaks, duration of symptoms before surgery, and the incidence of RRDCD were compared. A logistic regression analysis was used to determine potential risk factors for RRDCD.
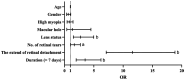
Results: Compared to the routine inpatient surgery group, the emergency surgery group had a significant less median time to surgery (P<0.001) and a decreased proportion of RRDCD (2.88% vs 10.84%, P<0.001). Logistic regression analysis revealed that a prolonged duration of RRD [OR 3.51, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.98-6.23], pseudophakia/aphakia status [OR 2.74, 95%CI (1.50-4.98)], multiple retinal breaks [OR 1.67, 95%CI (1.03-2.70)], and a substantial extent of RRD [OR 11.58, 95%CI (7.12-18.84)] were independent risk factors for RRDCD.
Conclusion: Emergency surgical pattern of RRD demonstrates a lower incidence of RRDCD. The adoption of an expedited surgical approach has the potential to reduce the duration of RRD, possibly correlating with a decreased risk of RRDCD development.
Keywords: ophthalmic emergency; rhegmatogenous retinal detachment; rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with choroidal detachment.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Gao K, None; Chen ZY, None; Lin ZL, None; Liu YP, None; Liu BY, None; Ma Y, None; Chen ZT, None; Tuxun R, None; Jiang L, None; Xu ZJ, None; Tsai CL, None; Lai KB, None; Li T, None.
Figures

References
-
- Li ZH, Li YH, Huang XH, et al. Quantitative analysis of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with choroidal detachment in Chinese using UBM. Retina. 2012;32(10):2020–2025. - PubMed
-
- Li PP, Li L, Wu JH. The effect of steroid intervention before vitrectomy for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with choroidal detachment: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Curr Eye Res. 2024;49(10):1005–1011. - PubMed
-
- Seelenfreund MH, Kraushar MF, Schepens CL, et al. Choroidal detachment associated with primary retinal detachment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974;91(4):254–258. - PubMed
-
- Luo SS, Xu HY, Yang LF, et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis of human vitreous in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with choroidal detachment by data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(6):1849–1863. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
