Genotype-phenotype analysis and functional study of three novel LRP6 variants in non-syndromic oligodontia
- PMID: 40534843
- PMCID: PMC12174413
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1598907
Genotype-phenotype analysis and functional study of three novel LRP6 variants in non-syndromic oligodontia
Abstract
Introduction: Tooth agenesis (TA) is a common craniofacial malformation in humans, characterized by the absence of one or more permanent teeth. Recent studies have identified the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) gene as an autosomal dominant contributor to TA. Herein we aimed to identify novel LRP6 variants in patients with non-syndromic oligodontia (NSO) and perform functional analyses of these variants.
Methods: Whole-exome sequencing (WES) was conducted on probands and their first-degree relatives to identify potential pathogenic variants. Identified LRP6 variants underwent computational pathogenicity prediction using integrated bioinformatics tools. Subcellular localization patterns were analyzed via immunofluorescence microscopy. Functional characterization of WNT/β-catenin signaling alterations was achieved through Western blot analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assays (TOP-Flash/FOP-Flash systems). Finally, genotype-phenotype correlations in LRP6-associated non-syndromic oligodontia (NSO) were systematically investigated.
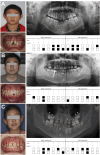
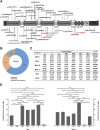
Results: We identified three novel LRP6 variations (NM_002336): a truncating variant [c.2182C>T (p.Arg728*)] and two missense variants [c.3773C>T (p.Thr1258Met) and c.1441C>T (p.Arg481Cys)]. Immunofluorescence characterization revealed that the missense variants exhibited subcellular localization patterns comparable to wild-type LRP6, with predominant distribution in the plasma membrane and cytoplasmic compartments. Western blot analysis revealed impaired β-catenin expression in cells harboring the LRP6 missense variants, suggesting compromised canonical WNT signaling pathway activity. Functional assessment using the TOP/FOP-Flash luciferase reporter system demonstrated significantly reduced TCF/LEF transcriptional activity associated with these variants, though statistical significance was exclusively observed for the Arg481Cys variant (P < 0.05). Literature review identified 39 LRP6 variants associated with 52 NSO patients, revealing that mandibular second premolars were the most frequently affected teeth, while maxillary first molars were least likely to be affected.
Discussion: We identified three novel LRP6 variants in patients with NSO from three Chinese families. Furthermore, we have confirmed through in vitro experiments that these novel LRP6 missense variants lead to impaired activation of the WNT signalling pathway. Finally, we summarized the genotype-phenotype correlation for LRP6-related NSO, finding that LRP6 variants are most likely to affect the mandibular second premolars.
Keywords: LRP6; genotype-phenotype; non-syndromic oligodontia; tooth agenesis; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2025 Yuan, Zhao, Meng, Zheng, Li, Ren, Li, Dou, Hou, Chen, Zhang, Ding and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel follicle-stimulating hormone receptor mutation causing primary ovarian failure: a fertility application of whole exome sequencing.Hum Reprod. 2016 Apr;31(4):905-14. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew025. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 26911863 Free PMC article.
-
Loss-of-function variants in GLMN are associated with generalized skin hyperpigmentation with or without glomuvenous malformation.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):107-116. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae108. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38489583
-
KREMEN1 Variants Associated with Ectodermal Dysplasia Impair Complex Formation of KREMEN1 with DKK1 and LRP6 and Attenuate WNT3A Response.J Invest Dermatol. 2025 Jun 17:S0022-202X(25)01853-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2025.05.036. Online ahead of print. J Invest Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40553753
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sociodemographic and Socioeconomic Determinants for the Usage of Digital Patient Portals in Hospitals: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Digital Divide.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 3;27:e68091. doi: 10.2196/68091. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40460427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basha M., Demeer B., Revencu N., Helaers R., Theys S., Bou S. S., et al. (2018). Whole exome sequencing identifies mutations in 10% of patients with familial non-syndromic cleft lip and/or palate in genes mutated in well-known syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 55, 449–458. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-105110 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

