Immune metabolic restoration in systemic lupus erythematosus: the impact of gut microbiota, probiotics, and nutritional synergy
- PMID: 40534849
- PMCID: PMC12173889
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602235
Immune metabolic restoration in systemic lupus erythematosus: the impact of gut microbiota, probiotics, and nutritional synergy
Abstract
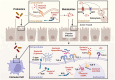
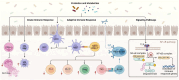
Gut microbiota alterations have been considered one of the attributes of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), and may offer an immunological disorder and even cause the disease. The probiotic administration, especially the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotics, is becoming highly utilized for the maintenance of the intestinal barrier's integrity and immune function, minimizing further the risks of developing some complications such as lupus nephritis, mechanisms that have remained so incompletely defined. This review focuses on the analysis of literature data about the influence of certain probiotic strains on the pathogenesis and course of SLE as immunomodulators and a new therapy strategy that seeks to achieve a synergistic effect with the help of an additional probiotic in combination with dietary supplements gingerols or vitamin D. The current review, therefore, provided the limitations in current trials addressing SLE and therapy optimization. The work is done with the intention of addressing the existing gaps in knowledge, thereby creating more space for new approaches to emerge toward the SLE management and improvement of patients' outcomes.
Keywords: 6-gingerol; gut microbiota; immune modulation; probiotics; systemic lupus erythematosus; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2025 Habiballah, Li and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yalavarthi S, Gould TJ, Rao AN, Mazza LF, Morris AE, Núñez-Álvarez C, et al. Release of neutrophil extracellular traps by neutrophils stimulated with antiphospholipid antibodies: A newly identified mechanism of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67:2990–3003. doi: 10.1002/art.39247 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Linden M, van den Hoogen LL, Westerlaken GHA, Fritsch-Stork RDE, van Roon JAG, Radstake T, et al. Neutrophil extracellular trap release is associated with antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and anti-phospholipid syndrome. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2018) 57:1228–34. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key067 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical