Serum extracellular vesicle microRNAs as potential biomarkers to predict pembrolizumab response and prognosis in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients
- PMID: 40534853
- PMCID: PMC12174437
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1540906
Serum extracellular vesicle microRNAs as potential biomarkers to predict pembrolizumab response and prognosis in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients
Abstract
Introduction: Circulating Extracellular Vesicles (cEVs) could represent new non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis in tumors. In the context of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) immunotherapy there's a great need for novel predictive and prognostic biomarkers. This study aims to analyze cEVs microRNAs in serum of advanced stage NSCLC patients with PD-L1 expression ≥50% at diagnosis, before first-line pembrolizumab, to evaluate their possible role as potential biomarkers for immunotherapy response prediction and outcomes.
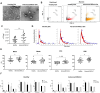
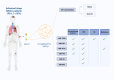
Methods: cEVs were isolated from serum of healthy subjects and NSCLC patients at diagnosis. All patients had tumor PD-L1≥50% and cEVs were extracted before first-line pembrolizumab treatment. cEVs were then characterized for morphology, integrity, concentration, size and protein contaminants. Subsequently, microRNA content (miR-10a, miR-21, miR-22, miR-30a, miR-34a, miR-106b, miR-125b, miR-150, miR-155, miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-451a) was investigated by digital PCR. Additionally, miRNA-targets and their roles were evaluated. All data were associated with immunotherapy response, Progression Free Survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG-PS) and metastases.
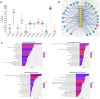
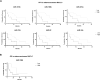
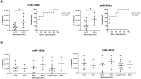
Results: Twelve NSCLC-related microRNAs have been found, for the first time, in serum cEVs from a specific cohort of metastatic advanced stage NSCLC patients. Through a functional analysis, these microRNAs are found to be connected to each other and involved in the pathology of NSCLC, particularly in IGF/P53/VEGF/NOTCH/PI3K pathways, in cytokine/interleukin signaling and in the immune system. Specifically, we demonstrated that cEV miR-106b, miR-451a, miR-181 and miR-10a were significantly up-regulated in non-responder patients compared to responder ones (p-value=0.08-0.1) predicting with high accuracy, already at diagnosis, treatment response. Furthermore, a low level of all these microRNAs predicted improved PFS (p-value=0.009-0.02) and a low amount of miR-106b predicted longer OS (p=0.069). In addition, it was observed that high levels of miR-106b and miR-451a are indicative of a high number of metastases (p=0.05/0.04, respectively) and of ECOG-PS=0.
Discussion: This is the first study that investigated specific potential serum cEV miRNAs to predict with high accuracy immunotherapy response and prognosis in specific metastatic NSCLC patients, already at diagnosis. Collectively, our cEV miRNA analysis identifies novel circulating biomarkers that are easily accessible and non-invasive, offering a potential blood-based tool to guide personalized medicine in NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC; biomarkers; extracellular vesicles; immunotherapy; liquid biopsy; microRNAs; prognosis; response prediction.
Copyright © 2025 Lamorte, De Luca, Tartarone, Trino, Giulivo, De Stradis, Maietti, Caivano and Laurenzana.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, alone or in combination with chemotherapy, as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lung Cancer. 2019 Aug;134:127-140. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.05.029. Epub 2019 May 30. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31319971
-
Circulating miR-125b is a novel biomarker for screening non-small-cell lung cancer and predicts poor prognosis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Dec;138(12):2045-50. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1285-0. Epub 2012 Jul 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22806310 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world outcomes of anti-PD1 antibodies in platinum-refractory, PD-L1-positive recurrent and/or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, and its potential practical predictors: first report from Korean Cancer Study Group LU19-05.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug;147(8):2459-2469. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03527-4. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33523301 Free PMC article.
-
Association of metabolomics with PD-1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy outcomes in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Apr 18;12(4):e008190. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008190. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38641349 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 expression in advanced NSCLC: Insights into risk stratification and treatment selection from a systematic literature review.Lung Cancer. 2017 Oct;112:200-215. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29191596
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

