Clinical and electrophysiological features of adult patients with combined central and peripheral demyelination- a systematic review
- PMID: 40534858
- PMCID: PMC12173897
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1572507
Clinical and electrophysiological features of adult patients with combined central and peripheral demyelination- a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The classification of combined central and peripheral demyelination (CCPD) is challenging due to unclear pathomechanisms and a lack of diagnostic and therapeutic criteria. Existing clinical data are limited to case reports or small series, with few attempts to define CCPD using radiological or molecular markers. Differential diagnosis depends on excluding well-characterized demyelinating diseases of the central and peripheral nervous systems. No systematic review has yet summarized the clinical, radiological, electrophysiological, molecular, and therapeutic evidence for CCPD.
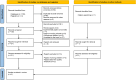
Methods: This review follows PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines, uses the JBI critical appraisal tool for case series and is registered at PROSPERO (CRD42025640575). A systematic search of Embase, MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Google Scholar was conducted for studies available up to December 2024. Inclusion criteria focused on adult patients with electrophysiological and imaging findings. Exclusion criteria included CCPD associated with infections, rheumatological conditions, or anti-MOG/anti-AQP4 antibodies.
Results: Most patients exhibited hemiparesis assessed by MMT and MRC scales, with tetraparesis often asymmetrical. Imaging revealed either diffuse CNS involvement (cerebral hemispheres, brainstem, spinal cord) or lesions limited to one or two sites. Nerve conduction studies showed primarily demyelinating features. Treatment frequently involved combination therapies.
Conclusions: This review underscores the dearth of high-quality data on CCPD, with extant studies frequently exhibiting a paucity of methodology for definitive analysis. The presence of elevated protein concentrations in CSF and the presence of antibodies, specifically anti-LacCer and anti-NF, has been identified as potential biomarkers of the disease. Furthermore, GCS in high doses might be one of the most effective treatment options.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42025640575, identifier CRD42025640575.
Keywords: combined central and peripheral demyelination (CCPD); encephalomyeloradiculoneuritis; lactosylceramide antibodies; myeloradiculoneuritis; neurofascin antibodies.
Copyright © 2025 Andrusiów, Dziadkowiak and Koszewicz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sociodemographic and Socioeconomic Determinants for the Usage of Digital Patient Portals in Hospitals: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Digital Divide.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 3;27:e68091. doi: 10.2196/68091. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40460427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions to Maintain HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria Service Delivery During Public Health Emergencies in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Protocol for a Systematic Review.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Jan 15;14:e64316. doi: 10.2196/64316. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39813677 Free PMC article.
-
Internet-Based Interventions for Preventing Premature Birth in Preconceptional Women of Childbearing Age: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 3;27:e60690. doi: 10.2196/60690. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40460430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Electroacupuncture in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: Protocol for a Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Nov 4;13:e55870. doi: 10.2196/55870. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39496309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papadopoulou M, Tzanetakos D, Moschovos C, Korona A, Vartzelis G, Voudris K, et al. Combined central and peripheral demyelination (CCPD) associated with MOG antibodies: report of four new cases and narrative review of the literature. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:3604. doi: 10.3390/JCM13123604/S1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical