Pan-cancer analysis reveals the potential role of DHCR24 in bladder cancer via interactions with HRAS to facilitate cholesterol synthesis
- PMID: 40535103
- PMCID: PMC12174751
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2025.15131
Pan-cancer analysis reveals the potential role of DHCR24 in bladder cancer via interactions with HRAS to facilitate cholesterol synthesis
Abstract
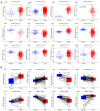
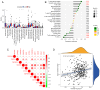
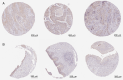
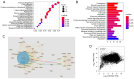
There is a strong association between cholesterol reprogramming and cancer development. However, 3β-hydroxysteroid Δ24-reductase (DHCR24), the final enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, has been relatively understudied in cancer progression. The present study aimed to perform a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of DHCR24 to elucidate its role across different malignancies. The interacting proteins of DHCR24 were identified by molecular docking node dynamics simulation. Duolink proximity ligation, cell viability and filipin staining assays were used to assess the function of DHCR24 in cancer cells and its underlying oncogenic mechanisms. The findings revealed that DHCR24 exhibits high expression in seven cancer types (bladder cancer, breast invasive carcinoma, liver hepatocellular carcinoma, prostate adenocarcinoma, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma, uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma and stomach adenocarcinoma), and low expression in five others (glioblastoma multiforme, kidney chromophobe, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma), suggesting that DHCR24 serves distinct roles depending on the cancer type. Notably, it was demonstrated that DHCR24 expression consistently increases with tumor stage and serves as an independent prognostic factor in BLCA. Moreover, molecular docking and kinetic modeling identified HRAS as a key interacting protein of DHCR24. The Duolink assay further demonstrated that DHCR24 interacts with HRAS outside the nucleus in 5637 human BLCA cells. Filipin fluorescence staining and cell proliferation assays also revealed that this interaction promoted cholesterol synthesis, contributing to cancer cell proliferation in the 5637 cells. In conclusion, the results of the present study provide novel insights into the oncogenic role of DHCR24 in BLCA and demonstrates its interaction with HRAS for the first time to the best of our knowledge, highlighting a potential mechanism driving tumor progression.
Keywords: BLCA; DHCR24; HRAS; cholesterol synthesis; pan-cancer analysis.
Copyright: © 2025 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
DHCR24 overexpression is involved in lipid metabolic reprogramming to drive cervical cancer malignant progression and is associated with immune microenvironment.BMC Cancer. 2025 Aug 9;25(1):1291. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14663-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40783686 Free PMC article.
-
DHCR24 is an independent predictor of progression in patients with non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma, and its functional role is involved in the aggressive properties of urothelial carcinoma cells.Ann Surg Oncol. 2014 Dec;21 Suppl 4:S538-45. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3560-6. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24562935
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis reveals NTN1 as an immune infiltrate risk factor and its potential prognostic value in SKCM.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85444-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863609 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Last AR, Ference JD, Menzel ER. Hyperlipidemia: Drugs for cardiovascular risk reduction in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95:78–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
