Intra- and peritumoral radiomics nomogram based on DCE-MRI for the early prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer
- PMID: 40535128
- PMCID: PMC12174392
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1561599
Intra- and peritumoral radiomics nomogram based on DCE-MRI for the early prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to create a nomogram model (NM) that combines clinical-radiological factors with radiomics features of both intra- and peritumoral regions extracted from pretherapy dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) images, in order to establish a reliable method for early prediction of pathological complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in patients with breast cancer.
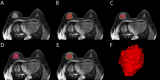
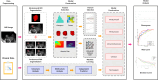
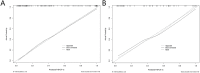
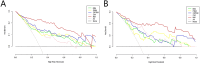
Methods: A total of 214 patients were randomly divided into a training set (n=149) and a test set (n=65) in a ratio of 7:3. Radiomics features were extracted from intratumoral region and 2-mm, 4-mm, 6-mm, 8-mm peritumoral regions on DCE-MRI images, and selected the optimal peritumoral region. The intratumoral radiomics model (IRM), 2-mm, 4-mm, 6-mm, 8-mm peritumoral radiomics model (PRM), the combined intra- and the optimal peritumoral radiomics model (CIPRM) were constructed based on five machine learning algorithms, and then the radiomics scores (Rad-score) were obtained. Independent risk factors for clinical-radiological features were obtained by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, and clinical model (CM) was constructed. Finally, the CIPRM Rad-score combined with clinical-radiological factors was used to construct a NM. The performance of different models were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis, calibration curve analysis, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
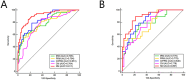
Results: In our study, the 6-mm peritumoral size was considered to be the optimal peritumoral region. The CM is constructed based on three independent risk factors: estrogen receptor (ER), Ki-67, and breast edema score (BES). Incorporating ER, Ki-67, BES, and CIPRM Rad-score (combined intra- and 6-mm peritumoral) into the nomogram achieved a reliable predictive performance. And the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the NM was 0.911, 0.848, 0.831, 0.826 for the training set and 0.897, 0.893, 0.784, 0.815 for the test set, respectively.
Conclusion: The NM has a good value for early prediction of pCR after NAC in breast cancer patients.
Keywords: breast cancer; intratumoral; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; nomogram; pathological complete response; peritumoral; radiomics.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Zhang, Wei, Yang, Wang, Wang, Fan, Sun and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Integrative Clinical and Intra- and Peritumoral MRI Radiomics Nomogram for the Preoperative Prediction of Lymphovascular Invasion in Rectal Cancer.Acad Radiol. 2025 Jul;32(7):3989-4001. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.02.019. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40044546
-
Multilayer perceptron deep learning radiomics model based on Gd-BOPTA MRI to identify vessels encapsulating tumor clusters in hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-center study.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Jul 7;25(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00895-9. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40624579 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics based on 2D ultrasound imaging in breast cancer was used to determine the optimal peritumoral range for predicting KI-67 expression.J Ultrasound. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.1007/s40477-025-01049-0. Online ahead of print. J Ultrasound. 2025. PMID: 40640519
-
Methodological issues in radiomics: impact on accuracy of MRI for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul;35(7):4325-4334. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11260-y. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39702630
-
A multimodal deep-learning model based on multichannel CT radiomics for predicting pathological grade of bladder cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jul;50(7):3049-3059. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04748-0. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39690281 Review.
References
-
- Guarneri V, Griguolo G, Miglietta F, Conte PF, Dieci MV, Girardi F. Survival after neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab-lapatinib and chemotherapy in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. ESMO Open. (2022) 7:100433. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100433 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

