Preoperative prediction of HER2 expression and sentinel lymph node status in breast cancer using a mammography radiomics model
- PMID: 40535132
- PMCID: PMC12174389
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1578458
Preoperative prediction of HER2 expression and sentinel lymph node status in breast cancer using a mammography radiomics model
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to develop and validate radiomic features derived from mammography (MG) to differentiate between various HER2 expression types (HER2-positive, HER2-low, and HER2-zero) and to preoperatively assess sentinel lymph node (SLN) status in breast cancer.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using clinicopathological and imaging data from 838 female breast cancer patients diagnosed at the Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University between January 2016 and September 2024. The patients were randomly divided into a training set (n=586) and a test set (n=252) in a 7:3 ratio. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified independent clinical predictors. Tumor segmentation and radiomic feature extraction were performed on mammography images. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method was applied for feature selection, and the radiomics model was developed. Model performance was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis.
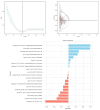
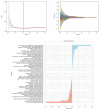
Results: There were no significant differences in clinicopathological factors and mammographic features between the training and test sets (P>0.05). Multivariate analysis identified ethnicity, lesion size, vascular tumor thrombus, clinical stage, tumor margin, and HER2 expression as independent predictors for SLN metastasis. Lesion size, PR expression, menopausal status, SLN metastasis, Ki67, CK5/6 expression, and calcification were independent predictors for HER2 expression. The SLN metastasis prediction model achieved AUCs of 0.84 in the training set and 0.83 in the test set. The HER2 expression model showed AUCs of 0.87 (positive), 0.82 (low), and 0.85 (zero) in the training set, and 0.84 (positive), 0.78 (low), and 0.84 (zero) in the test set.
Conclusion: Radiomic features based on mammography can effectively preoperatively predict SLN status and HER2 expression types in breast cancer, offering valuable insights for individualized treatment strategies.
Keywords: HER2 expression; breast cancer; mammography; radiomics; sentinel lymph node.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Yuan, Song, Liu, Chen, Wang, Dong and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prediction of HER2 expression in breast cancer patients based on multi-parametric MRI intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics features combined with clinical and imaging indicators.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 9;15:1531553. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1531553. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40552272 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Radiomics for the Prediction of Breast Cancers with HER2-Zero, -Low, and -Positive Status: A Dual-Center Study.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241292668. doi: 10.1177/15330338241292668. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39470030 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-based radiomic nomogram for predicting the invasive status of breast cancer: a multicenter study.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 1;30(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02828-5. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40598678 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating multimodal ultrasound imaging for improved radiomics sentinel lymph node assessment in breast cancer.Gland Surg. 2025 Jul 31;14(7):1348-1365. doi: 10.21037/gs-2025-223. Epub 2025 Jul 25. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40771387 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Modality Virtual Biopsy System Integrating MRI and MG for Noninvasive Predicting HER2 Status in Breast Cancer.Acad Radiol. 2025 Jul;32(7):3858-3869. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.02.039. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40068996
References
-
- Joshi RM, Telang B, Soni G, Khalife A. Overview of perspectives on cancer, newer therapies, and future directions. Endoscopic Ultrasound. (2024) 10:105–9. doi: 10.1097/ot9.0000000000000039 - DOI
-
- Zha HL, Zong M, Liu XP, Pan JZ, Wang H, Gong HY, et al. Preoperative ultrasound-based radiomics score can improve the accuracy of the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center nomogram for predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Eur J Radiol. (2021) 135:109512. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109512 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

