Development and validation of a clinical model to predict low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia in chronic atrophic gastritis patients: a retrospective observational multicenter analysis
- PMID: 40535142
- PMCID: PMC12173873
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1597099
Development and validation of a clinical model to predict low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia in chronic atrophic gastritis patients: a retrospective observational multicenter analysis
Abstract
Background: Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG), an early stage of gastric cancer, is a major digestive disorder, and the prognosis of CAG is determined by many sociodemographic and clinicopathologic subject characteristics. This retrospective observational multicenter analysis was conducted to explore risk factors and construct a predictive model for low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (LGIN) in patients with CAG.
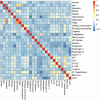
Methods: The training dataset included 317 CAG patients diagnosed and treated in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine from September 2018 to January 2025. All the baseline characteristics, including gender, age, education, basic diseases, blood indicators, and pathological mechanism during treatment of CAG, were recorded and selected based on both the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis with 10-fold cross-validation and logistic regression analysis. After that, the nomogram was established, and its accuracy and predictive performance were evaluated via the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC), calibration curves, Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, and decision curve analysis (DCA) curves. For the validation dataset, the medical record information of 92 CAG patients diagnosed and treated in the Hefei Second People's Hospital from November 2023 to January 2025 was recorded for subsequent analysis.
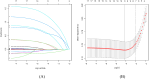
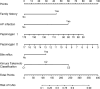
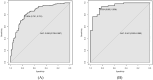
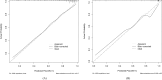
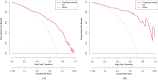
Results: Our LASSO regression analysis revealed that family history, HP infection, pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II, bile reflux, and Kimura-Takemoto classification (C3 vs. C1) were significant independent risk factors, and the fitting equation was obtained. A nomogram for predicting LGIN in CAG patients was established. The ROC curve revealed that our predictive model showed good predictive efficacy with an AUC value of 0.838 (95% CI = 0.789-0.887) with a specificity of 0.761 and a sensitivity of 0.791 in the training dataset and an AUC value of 0.941 (95% CI = 0.893-0.989) with a specificity of 0.852 and a sensitivity of 0.908 in the validation dataset. Moreover, calibration and DCA curves demonstrated that our predictive model had a good fit, better net benefit, and predictive efficiency in LGIN in CAG patients.
Conclusions: Our predictive model demonstrated that family history, HP infection, pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II, bile reflux, and Kimura-Takemoto classification were the independent risk factors of LGIN in CAG patients with high accuracy and good calibration.
Keywords: chronic atrophic gastritis; low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; multi-center retrospective analysis; nomogram; predictive model.
Copyright © 2025 Ding, Zhang, Chen, Gao, Xu, Pei, Zhang, Song and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and validation of a clinical predictive model for chronic atrophic gastritis in patients: a multi-center retrospective analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 19;12:1570893. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1570893. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40612582 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nomogram for predicting osteoporosis with low back pain among the patients in Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture of China.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 5;16:1535163. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1535163. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40538801 Free PMC article.
-
[Prediction model for transformation of chronic atrophic gastritis to high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia based on traditional Chinese medicine syndrome patterns].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 May 25;54(3):297-306. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2024-0542. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40394917 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in cutaneous malignant melanoma: a proportional meta-analysis and regression.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):24-35. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae011. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38197404
-
Development and validation of an AMR-based predictive model for post-PCI contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 26;12:1552762. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1552762. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40642748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hagiwara T, Mukaisho K, Nakayama T, Sugihara H, Hattori T. Long-term proton pump inhibitor administration worsens atrophic corpus gastritis and promotes adenocarcinoma development in Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori. Gut. (2011) 60:624–30. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.207662 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

