Effects of mind-body exercise in chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea patients-a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40535150
- PMCID: PMC12174109
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1546996
Effects of mind-body exercise in chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea patients-a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: The objective of this meta-analysis is to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of various mind-body exercises in the rehabilitation of individuals with chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea.
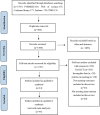
Design: A systematic review and network meta-analysis was conducted on articles from PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and China National Knowledge infrastructure which were searched up to November 21, 2024. The methodological quality of the included trials was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. A network meta-analysis was performed to compare the effects of various mind-body therapies, including Liuzijue, Baduanjin, Yoga, Tai Chi, Wuqinxi, Qigong, Yijinjing, and Buddhist walking meditation.
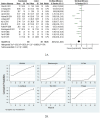
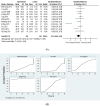
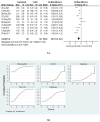
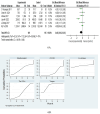
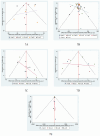
Results: The analysis included 44 randomized controlled trials involving a total of 2,957 subjects. The network meta-analysis indicated that Yoga might be the most effective exercise intervention for reducing the MLHFQ score (SUCRA: 71.8%). Yoga training demonstrated superior results in increasing the 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) (SUCRA: 99.7%). Qigong was also identified as the most effective exercise intervention for decreasing St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) (SUCRA: 97.1%). When compared with other treatments, Baduanjin is likely the most appropriate intervention for decreasing COPD Assessment Test (CAT) (SUCRA: 87.1%). Regarding N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), Yoga might be more advantageous for decreasing the NT-proBNP (SUCRA: 83.4%).
Conclusion: The findings of this study suggest that mind-body exercise may represent a promising intervention for the management of chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea. Our findings indicate that Yoga might be the most effective exercise intervention for improving the MLHFQ scores, 6MWD, and NT-proBNP. Qigong is identified as the most effective exercise intervention for decreasing SGRQ. Compared to other treatment methods, Baduanjin may be the most suitable intervention for lowering CAT. This study recommends that patients with chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea select appropriate mind-body exercises to achieve effective management of chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea.
Systematic review registration: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2024-11-0092/, INPLASY INPLASY2020100052.
Keywords: chronic cardiopulmonary dyspnoea; exercise interventions; mind-body exercises; network meta-analysis; yoga.
© 2025 Li, Wu and Lei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Campbell P, Rutten FH, Lee MM, Hawkins NM, Petrie MC. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: everything the clinician needs to know. Lancet. (2024) 403(10431):1083–92. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02756-3 Erratum in: Lancet. 2024 March 16;403(10431):1026. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00494-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

