Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- PMID: 40535170
- PMCID: PMC12176012
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2025-1117
Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
Abstract
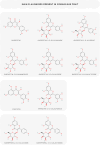
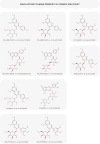
Although cornelian cherry is an underutilized fruit species, its fruits have a high biological value due to valuable biologically active substances, especially polyphenols. The total content of polyphenols accounts for 37% of all the bioactive substances examined. Flavonols, anthocyanins, flavan-3-ols, and phenolic acids represent the main groups of phenolic compounds present and thanks to these compounds, cornelian cherry fruits possess mainly antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, metabolic, antidiabetic, cardioprotective, and anticancer effects. This review summarizes new research aimed at popularizing this lesser-known species not only for direct consumption but also for further processing.
Keywords: Cornus mas; anti-inflammatory; anticancer effect; antidiabetic; antimicrobial; metabolic; polyphenols.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bayram HM, Ozturkcan SA. Bioactive components and biological properties of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.): A comprehensive review. J Funct Foods. 2020;75:104252.
-
- Jurecková Z, Divis P, Cetkovská J, Vespalcová M, Porízka J, Rezníček V. Fruit characteristics of different varieties of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) cultivated in the Czech Republic. Erwerbs-Obstbau. 2021;63:143–9.
-
- De Biaggi M, Donno D, Mellano MG, Riondato I, Rakotoniaina EN, Beccaro GL. Cornus mas (L.) fruit as a potential source of natural health-promoting compounds: physico-chemical characterisation of bioactive components. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2018;73:89–94. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources