Effects of physical exercise on college students' sense of meaning in life: the chain mediating role of stress perception and mental toughness
- PMID: 40535180
- PMCID: PMC12174108
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1612957
Effects of physical exercise on college students' sense of meaning in life: the chain mediating role of stress perception and mental toughness
Abstract
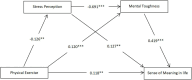
Physical exercise has a significant effect on college students' sense of meaning in life, and is an important way to promote college students' mental health and enhance their sense of meaning in life. To explore the relationship between stress perception, mental toughness in college students' physical exercise and college students' sense of meaning in life. The scale was used to measure 604 college students and statistically analyzed using SPSS29.0 and Process 4.1. The results showed that the direct positive effect of physical exercise on college students' sense of meaning in life was significant (effect value = 0.00297, accounting for 62.39% of the total effect). Through the independent mediation path, physical exercise can indirectly affect the sense of meaning of life by decreasing stress perception (negative mediation effect value = -0.00040, accounting for -8.40%) and enhancing mental toughness (positive mediation effect value = 0.00127, accounting for 26.68%). In addition, the chain-mediated path (physical exercise → stress perception → mental toughness → sense of meaning in life) effect of stress perception and mental toughness was significant (effect value = 0.00092, accounting for 19.33%), suggesting that physical exercise first relieves stress perception, then enhances mental toughness, and ultimately enhances the sense of meaning in life. To summarize, physical exercise positively predicts the sense of meaning of life through direct action, and also forms a multiple mechanism of "stress reduction - toughness enhancement - meaning enhancement" through the negative intermediary of stress perception, the positive intermediary of mental toughness, and the chain intermediary effect of the two. Meanwhile, it provides theoretical references for the enhancement of college students' sense of meaning in life and the improvement of sports health promotion programs.
Keywords: intermediary effect; mental toughness; physical exercise; sense of meaning in life; stress perception.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The chain mediating role of emotion regulation and stress perception in physical activity alleviating college students' health anxiety.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 9;15(1):29189. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14481-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40783609 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of physical exercise on college students' pro-social behavior: the chain mediating role of sense of meaning in life and subjective well-being.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1604700. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1604700. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40606900 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between physical exercise and suicidal ideation in college students: chain mediating effect of basic psychological needs satisfaction and sense of meaning in life.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1450031. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1450031. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40642043 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Language Processing Chatbot-Based Interventions for Improvement of Diet, Physical Activity, and Tobacco Smoking Behaviors: Systematic Review.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025 Jun 11;13:e66403. doi: 10.2196/66403. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025. PMID: 40503914 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson R. J., Brice S. (2011). The mood-enhancing benefits of exercise: memory biases augment the effect. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 12, 79–82. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2010.08.003 - DOI
-
- Belcher B. R., Zink J., Azad A., Campbell C. E., Chakravartti S. P., Herting M. M. (2021). The roles of physical activity, exercise, and fitness in promoting resilience during adolescence: effects on mental well-being and brain development. Biol. Psychiatry 6, 225–237. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2020.08.005, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ding S., Xiao R., Zhang Z. (2016). The relationship between college students' sports activities and sense of meaning in life. Chin. J. Sch. Health 37, 445–448. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2016.03.037 - DOI
-
- Feng B., Li Z., Wang K., Cui H. (2022). The relationship between college students' life goals and psychological resilience: the multiple mediating effects of self-control and general self-efficacy. Psychol. Res. 15, 78–85. doi: 10.19988/j.cnki.issn.2095-1159.2022.01.010 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources