Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in recurrent pregnancy loss: a retrospective analysis of patients with abnormal cellular immunity
- PMID: 40535341
- PMCID: PMC12173927
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1546602
Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in recurrent pregnancy loss: a retrospective analysis of patients with abnormal cellular immunity
Abstract
Introduction: Various causes of recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) have been identified, but even with a detailed evaluation, almost half of the cases have unidentified etiologies. Immune imbalance is one of the proposed potential etiologies of these idiopathic RPL. To regulate abnormal cellular immunity, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), a type of immunotherapy, is proposed to improve pregnancy outcomes. However, the efficacy of IVIG in RPL is still controversial.
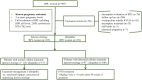
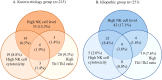
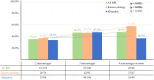
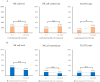
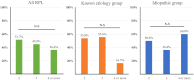
Methods: RPL was defined as women with two or more spontaneous abortions and in total, 987 RPL women visited Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Konyang University Hospital from January 2007 to December 2020. Only those with a full evaluation and known treatment outcome were included. Idiopathic RPL(n=215) and women with known etiology (n=251) were enrolled. Both the idiopathic and known etiology groups were subsequently stratified into subgroups based on the presence of at least one abnormal cellular immunity (n=100 and n=97, respectively). We investigated the pregnancy outcome by sorting the patients into seven subgroups depending on abnormal cellular immunity including natural killer (NK) cell level, NK cell cytotoxicity and Th1/Th2 ratio.
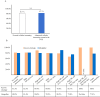
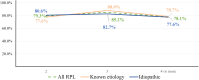
Results: Patients with older age and higher body mass index had negative effect on pregnancy outcomes whereas the number of previous miscarriages did not show significant difference in pregnancy outcomes. Among all RPL women with at least one abnormal cellular immunity were treated with IVIG and the overall live birth rate (LBR) was 82.7%. The group which did not have IVIG treatment showed an overall LBR of 80.7%. Among the seven groups of idiopathic RPL women with abnormal cellular immunity, the group with both high NK cell level and NK cell cytotoxicity showed the highest LBR, 90.5%, and the group with both high NK cell level and Th1/Th2 ratio showed the lowest LBR, 75%.
Discussion: IVIG treatment appears to improve LBRs in women with RPL and abnormal cellular immunity. These findings support the potential benefit of IVIG in selected RPL patients with immune imbalances. Further studies are needed to refine patient selection criteria and optimize treatment protocols for improving pregnancy outcomes in this population.
Keywords: TH1/TH2 ratio; immunity; intravenous immunoglobulin; natural killer cell cytotoxicity; natural killer cells; recurrent pregnancy loss.
Copyright © 2025 Han, Park, Kim and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Berek JS. Berek&Novak’s gynecology. 16 ed. Berek JS, editor. Wolters Kluwer at Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; (2019).
-
- Yamada H, Deguchi M, Saito S, Takeshita T, Mitsui M, Saito T, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in women with four or more recurrent pregnancy losses: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. EClinicalMedicine. (2022) 50:101527. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101527 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

