Extracellular vesicles in reproductive biology and disorders: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40535345
- PMCID: PMC12173914
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1550068
Extracellular vesicles in reproductive biology and disorders: a comprehensive review
Abstract
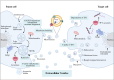
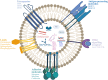
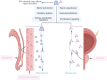
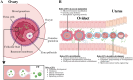
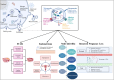
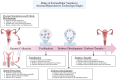
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) facilitate intercellular communication and the conveyance of bioactive substances, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. They play a significant role in various reproductive biological processes, including gametogenesis, fertilization, early embryo development, and implantation. Dysfunctional EV activity is associated with various reproductive diseases, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, male infertility, and recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). This review systematically examines and categorizes current knowledge on EV functions in reproductive biology and disorders, and their potential as diagnostic and therapeutic tools. A systematic literature search from 2000 to 2024 identified studies showing EVs' influence on gamete maturation, fertilization, embryonic development, and implantation. They also play a role in reproductive disorders by affecting insulin resistance, androgen production, inflammation, angiogenesis, sperm quality, and maternal-fetal immune tolerance. The review concludes that EVs are integral to reproductive health, with further research needed to understand their mechanisms and clinical potential.
Keywords: embryo implantation; embryos; extracellular vesicles; fertility; oocyte; reproductive disorders; sperm.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Zhang, Sun, Yi, Han, Zhao, Zhang and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

