H&E Style Translation Using CycleGAN for Deep Ultraviolet-Excitation Fluorescence Images of Pancreatic Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration/Biopsy Toward Slide-Free Rapid Pathology
- PMID: 40535473
- PMCID: PMC12173637
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.25-00007
H&E Style Translation Using CycleGAN for Deep Ultraviolet-Excitation Fluorescence Images of Pancreatic Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration/Biopsy Toward Slide-Free Rapid Pathology
Abstract
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration/biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) is critical for determining treatment strategies for patients with pancreatic cancer. However, conventional pathological examination using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is time-consuming. Microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation (MUSE) enables rapid pathological diagnosis without requiring slide preparation. This study explores the potential of combining MUSE imaging with a cycle-consistent generative adversarial network (CycleGAN), an image generation algorithm capable of learning translations without paired images, to enhance diagnostic workflows for pancreatic EUS-FNA/B. Thirty-five pancreatic specimens were stained with Terbium/Hoechst 33342, and deep ultraviolet (DUV) fluorescence images were captured by exciting the tissue surface. These fluorescence images, along with H&E-stained formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) sections from the same specimens, were divided into 256 × 256-pixel segments for CycleGAN training. The algorithm was employed to translate pseudo-H&E images from MUSE test images. The pseudo-H&E images generated by the CycleGAN showed improved inter-pathologist agreement among three pathologists compared with the original MUSE images. We established a technique to perform MUSE imaging on small pancreatic samples obtained through EUS-FNA/B and confirmed that H&E-style translation using CycleGAN simplified interpretation for pathologists. Integrating MUSE imaging with CycleGAN has the potential to offer a rapid, cost-effective, and accurate diagnostic tool.
Keywords: cycle-consistent generative adversarial network (CycleGAN); endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration/biopsy (EUS-FNA/B); microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation (MUSE); pancreatic cancer; rapid pathological diagnosis.
2025 The Japan Society of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
VT.T. received a research grant from Terasaki Electric Co., Ltd.
Figures
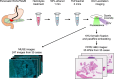

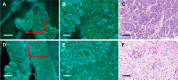
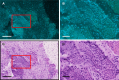
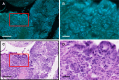
Similar articles
-
Exploratory multi-cohort, multi-reader study on the clinical utility of a deep learning model for transforming cryosectioned to formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) images in breast lesion diagnosis.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 17;27(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02064-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40528232 Free PMC article.
-
EUS FNAC without rapid on-site evaluation is comparable to EUS FNB with macroscopic on-site evaluation in evaluation of intra-abdominal masses.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun;44(3):371-377. doi: 10.1007/s12664-025-01741-3. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39969684
-
Intelligent Diagnosis of Pancreatic Biopsy From Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Via Stimulated Raman Histopathology.Lab Invest. 2025 Aug;105(8):104182. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2025.104182. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Lab Invest. 2025. PMID: 40288652
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic core-needle/microforceps biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool for pancreatic lesions: Experience from a large academic institution.Am J Clin Pathol. 2025 Sep 9;164(3):351-359. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaf050. Am J Clin Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40414818
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matsuda T, Ajiki W, Marugame T, Ioka A, Tsukuma H, Sobue T, et al. Population-Based Survival of Cancer Patients Diagnosed Between 1993 and 1999 in Japan: A Chronological and International Comparative Study. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011;41:40–51. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Hewitt MJ, McPhail MJ, Possamai L, Dhar A, Vlavianos P, Monahan KJ. EUS-Guided FNA for Diagnosis of Solid Pancreatic Neoplasms: A Meta-Analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:319–331. - PubMed
-
- Puli SR, Bechtold ML, Buxbaum JL, Eloubeidi MA. How Good Is Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration in Diagnosing the Correct Etiology for a Solid Pancreatic Mass?: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Pancreas. 2013;42:20–26. - PubMed

