Distinct trajectory patterns of neutrophil-to-albumin ratio predict clinical outcomes after endovascular therapy in large vessel occlusion stroke
- PMID: 40535510
- PMCID: PMC12174067
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1570662
Distinct trajectory patterns of neutrophil-to-albumin ratio predict clinical outcomes after endovascular therapy in large vessel occlusion stroke
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the dynamic characteristics and prognostic value of neutrophil-to-albumin ratio (NAR) in patients with acute large vessel occlusion ischemic stroke (LVO-AIS) undergoing endovascular therapy (EVT).
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we consecutively enrolled 299 patients with anterior circulation LVO-AIS who underwent EVT between January 2018 and February 2024. NAR was measured at admission, day 1, and day 3 after EVT. The primary outcome was poor functional outcome at 90 days (modified Rankin Scale score 3-6). Secondary outcomes included symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), malignant cerebral edema (MCE), and in-hospital mortality (IHM). Multivariable logistic regression and restricted cubic spline regression were used to analyze the association between NAR and functional outcomes. Latent class trajectory modeling (LCTM) was applied to identify NAR evolution patterns, and propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to balance baseline characteristics between different trajectory groups, followed by conditional logistic regression to assess their association with clinical outcomes.
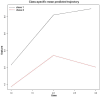
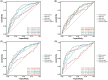
Results: At 90-day follow-up, 197 patients (65.9%) had poor outcomes. The predictive value of NAR increased over time, with day 3 NAR showing the best predictive performance (poor outcome: AUC = 0.79; sICH: AUC = 0.70; MCE: AUC = 0.75; IHM: AUC = 0.81). Multivariable analysis showed that for each unit increase in day 3 NAR, the risk of 90-day poor outcome increased 2.81-fold (95% CI: 1.96-4.03, p < 0.001). LCTM analysis identified two distinct NAR evolution patterns: continuously increasing (31.1%) and peak-then-decline (68.7%). After PSM (63 patients per group), compared with the continuously increasing trajectory, the peak-then-decline trajectory was associated with significantly lower risks of poor functional outcome (OR = 0.38, 95% CI: 0.17-0.86, p = 0.020), sICH (OR = 0.38, 95% CI: 0.17-0.86, p = 0.020), MCE (OR = 0.25, 95% CI: 0.10-0.61, p = 0.002), and IHM (OR = 0.13, 95% CI: 0.04-0.42, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: NAR trajectory patterns independently predict clinical outcomes after EVT for LVO-AIS. Dynamic monitoring of NAR, particularly on day 3 post-procedure, may facilitate early risk stratification and development of targeted intervention strategies, providing a new biomarker tool for precision stroke management.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; clinical outcomes; endovascular therapy; large vessel occlusion stroke; latent class trajectory modeling; neutrophil-to-albumin ratio; propensity score matching.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Sun, Yu, She, Zhao, Cai, Chen and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Objective nutritional indices as an independent predictor of functional outcome after endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a cohort study in a Chinese population.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 18;12:1504208. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1504208. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40607035 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinflammatory biomarkers as predictors of hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke patients after endovascular thrombectomy.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 13;16:1606563. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1606563. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40584526 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic serum lactate dehydrogenase monitoring during the acute phase and association with in-hospital all-cause mortality risk in large vessel occlusion acute ischemic stroke patients.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 13;30(1):743. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-03025-0. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40796897 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular thrombectomy after acute ischemic stroke of the basilar artery: a meta-analysis of four randomized controlled trials.J Neurointerv Surg. 2023 Dec 21;15(e3):e446-e451. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2022-019776. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023. PMID: 36597942
-
Safety and efficacy of adjunctive intra-arterial antithrombotic therapy during endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurointerv Surg. 2025 Jun 1;17(e2):e237-e244. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2023-021244. J Neurointerv Surg. 2025. PMID: 38253378
Cited by
-
Machine learning-based predictive model for acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury: a retrospective analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 12;12:1638097. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1638097. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40873797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akpınar C. K., Kocaturk O., Aykac O., Acar B. A., Dogan H., Onalan A., et al. (2023). Can C-reactive protein/albumin ratio be a prognostic factor in acute stroke patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 231:107856. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2023.107856, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Artigas A., Wernerman J., Arroyo V., Vincent J. L., Levy M. (2016). Role of albumin in diseases associated with severe systemic inflammation: pathophysiologic and clinical evidence in sepsis and in decompensated cirrhosis. J. Crit. Care 33, 62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.12.019, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

