Association between sarcopenic obesity and dementia in the Chinese elderly using different definitions of obesity: evidence from the CHARLS
- PMID: 40535512
- PMCID: PMC12174056
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1540272
Association between sarcopenic obesity and dementia in the Chinese elderly using different definitions of obesity: evidence from the CHARLS
Abstract
Objectives: The prevalence of sarcopenic obesity, characterized by the coexistence of reduced muscle mass and function alongside increased adipose tissue, is increasing in the aging population. This study aims to investigate the association between sarcopenic obesity and dementia risk in community-dwelling older adults in China, utilizing a nationally representative dataset. Furthermore, we aim to assess the comparative effectiveness of waist circumference versus body mass index as indicators for assessing this risk association.
Design: The study was designed as a cross-sectional study.
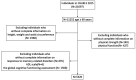
Setting and participants: Based on the nationally representative data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) 2015, a total of 5,320 community-dwelling participants aged 60 years and above were categorized into four groups according to their respective classifications of normal status, possible sarcopenia, obesity, and sarcopenic obesity.
Methods: Multivariable logistic regression models were used to analyze the relationship between sarcopenic obesity and probable dementia while adjusting for potential confounders.
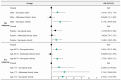
Results: After adjusting for potential confounders, possible sarcopenia alone (OR 1.674, 95% CI 1.238-2.264) and sarcopenic obesity (OR 1.812, 95% CI 1.325-2.479) were significantly associated with an increased risk of probable dementia. In contrast, abdominal obesity alone, defined by waist circumference (WC), was not significantly associated with dementia risk. When stratified by age and gender, the association between sarcopenic obesity and probable dementia remained significant.
Conclusion and implications: The findings from this cross-sectional study suggest that both possible sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity are significantly associated with an increased risk of probable dementia among older adults residing in the community in China. Notably, the relationship between sarcopenic obesity and dementia appears to be more pronounced compared to either possible sarcopenia or obesity alone. Moreover, incorporating waist circumference alongside components of possible sarcopenia may serve as a more effective predictor of cognitive impairment when compared to relying solely on body mass index (BMI). These results underscore the critical importance of early identification and intervention for individuals with sarcopenic obesity to mitigate the risk of developing dementia.
Keywords: CHARLS; cross-sectional study; dementia; probable sarcopenia; sarcopenic obesity.
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Xiang, Jia and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

