Establishment and epidemiological investigation of a dual fluorescent qPCR assay for Pasteurella multocida and Salmonella in yaks in the Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Garzê, China
- PMID: 40535542
- PMCID: PMC12174084
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1599817
Establishment and epidemiological investigation of a dual fluorescent qPCR assay for Pasteurella multocida and Salmonella in yaks in the Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Garzê, China
Abstract
Introduction: Yaks serve as a vital economic and ecological resource in high-altitude regions, but it faces significant health challenges from various pathogens. Among these, Pasteurella multocida and Salmonella are critical pathogens that contribute to severe diseases.
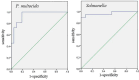
Methods: A duplex real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR assay was developed to simultaneously detect Pasteurella multocida and Salmonella. The species-specific genes kmt1 and invA were selected as target regions for primer and probe design. Following rigorous optimization, a duplex assay was established. Recombinant plasmids were constructed to serve as standards for generating standard curves. The detection thresholds were determined using SPSS statistical analysis and receiver operating characteristic curve methods. Furthermore, the assay's sensitivity, specificity, stability, and clinical applicability were evaluated.
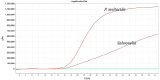
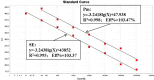
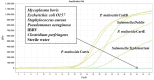
Results: The established assay demonstrated high sensitivity, with detection limits of 100 and 10 copies for pMD-kmt1 and pMD-invA, respectively. No cross-reactivity was observed with six pathogens, including Mycoplasma bovis, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and others. The standard curves showed strong linearity, with coefficients of determination of 0.995 and 0.998, and amplification efficiencies of 103.37% and 103.47% for pMD-kmt1 and pMD-invA, respectively. No interference was observed between high- and low-concentration templates during simultaneous detection. The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation ranged from 0.23% to 1.51%. Detection thresholds were determined to be cycle threshold values of 41.5 for P. multocida and 40.0 for Salmonella. Clinical evaluation was performed on 226 samples collected from yaks in seven counties of Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan Province, China. The single infection rates of P. multocida and Salmonella were 20.35% (46/226) and 38.50% (87/226), respectively, while the co-infection rate was 6.19% (14/226).
Discussion: This study successfully established a duplex real-time fluorescence PCR assay that enables the simultaneous detection of P. multocida and Salmonella with high sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency. The assay offers a reliable and rapid diagnostic tool that is particularly suited for clinical and epidemiological investigations in yak populations.
Keywords: Pasteurella multocida; Salmonella; detection; duplex real-time fluorescence PCR; yak.
Copyright © 2025 Pan, Yu, Wang, Li, Tian, Xin, Hu, Xiao, Liu, Zhu, Lan, Zhu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A quadruplex real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method for identification and serotyping of Pasteurella multocida.Microb Pathog. 2025 Oct;207:107889. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107889. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40639696
-
The quadruplex fluorescent quantitative PCR method for the simultaneous detection of respiratory diseases in quail: Pasteurella multocida, Avibacterium paragallinarum, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Mycoplasma synoviae.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1605356. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1605356. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40661987 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of virulence and resistance genes in Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from dairy cattle with and without bovine respiratory disease.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0120025. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01200-25. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40522106 Free PMC article.
-
Post-mortem diagnosis of septic arthritis by Pasteurella multocida: a case report and literature review of fatal septic arthritis.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025 Jun;21(2):787-806. doi: 10.1007/s12024-024-00929-x. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39797963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in cutaneous malignant melanoma: a proportional meta-analysis and regression.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):24-35. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae011. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38197404
References
-
- Almoheer R., Abd Wahid M. E., Zakaria H. A., Jonet M. A. B., Al-Shaibani M. M., Al-Gheethi A., et al. (2022). Spatial, temporal, and demographic patterns in the prevalence of hemorrhagic septicemia in 41 countries in 2005-2019: A systematic analysis with special focus on the potential development of a new-generation vaccine. Vaccines (Basel) 10. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020315 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

