Assessment of synthetic post-therapeutic OCT images using the generative adversarial network in patients with macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion
- PMID: 40535568
- PMCID: PMC12174594
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1609567
Assessment of synthetic post-therapeutic OCT images using the generative adversarial network in patients with macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study is to generate post-therapeutic optical coherence tomography (OCT) images based on pre-therapeutic OCT by using generative adversarial networks (GANs). The synthetic images enable us to predict the short-term therapeutic efficacy of intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in retinal vein occlusion (RVO) patients.
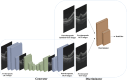
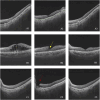
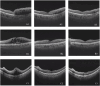
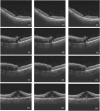
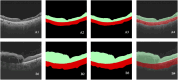
Methods: The study involved patients with RVO who received intravitreal anti-VEGF injection from 1 November 2018 to 30 November 2019. The OCT images taken before and shortly after treatment, with an interval of 4-8 weeks, were collected and randomly divided into the training set and test set at a ratio of approximately 3:1. The model is constructed based on the pix2pixHD algorithm, and synthetic OCT images are evaluated in terms of the picture quality, authenticity, the central retinal thickness (CRT), the maximal retinal thickness, the area of intraretinal cystoid fluid (IRC), and the area of subretinal fluid (SRF). Three supporting models, namely, the macular detection model, retinal stratification model, and lesion detection model, were constructed. Segmentation of macular location, retinal structure, and typical lesions were added to the input information. After verifying their accuracy, supporting models were used to detect the CRT, the maximal retinal thickness, IRC area, and SRF area of synthetic OCT images. The output predictive values are compared with real data according to the annotation on the real post-therapeutic OCT images.
Results: A total of 1,140 pairs of pre- and post-therapeutic OCT images obtained from 95 RVO eyes were included in the study, and 374 images were annotated. Of the synthetic images, 88% were considered to be qualified. The accuracy of discrimination of real versus synthetic OCT images was 0.56 and 0.44 for two retinal specialists, respectively. The accuracy to predict the treatment efficacy of CRT, the maximal retinal thickness, IRC area, and SRF area was 0.70, 0.70, 0.92, and 0.78, respectively.
Conclusion: Our study proves that the GAN is a reliable tool to predict the therapeutic efficacy of anti-VEGF injections in RVO patients. Evaluations conducted both qualitatively and quantitatively indicated that our model can generate high-quality post-therapeutic OCT images. Consequently, it has great potential in predicting the treatment efficacy and providing guidance to clinical decision-making.
Keywords: anti-vascular endothelial growth factor; generative adversarial networks; optical coherent tomography; retinal vein occlusion; therapeutic efficacy prediction.
Copyright © 2025 Feng, Yang, Zhao, Zhao, Du, Yu, Ding, Li and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors JZ, YD and DD were employed by company Visionary Intelligence Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Costa J. V., Moura-Coelho N., Abreu A. C., Neves P., Ornelas M., Furtado M. J. (2021). Macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion in a real-life setting: a multicenter, nationwide, 3-year follow-up study. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 259 (2), 343–350. 10.1007/s00417-020-04932-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horozoglu F., Sener H., Polat O. A., Temizyurek O., Evereklioglu C. (2023). Predictive impact of optical coherence tomography biomarkers in anti-vascular endothelial growth factor resistant macular edema treated with dexamethasone implant. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 42, 103167. 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2022.103167 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

