Metabolic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma - a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40535577
- PMCID: PMC12171862
- DOI: 10.3205/iprs000190
Metabolic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma - a comprehensive review
Abstract
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide with an increasing incidence. The surgical treatment is challenging and often requires the entire repertoire of plastic surgery. Diagnostically only a few crucial parameters are in use and even less for an individual and specific drug targeting. An individualised prognostic calculation is unavoidable to be able to adapt very complex surgical processes to an acceptable level. Unfortunately, the classic TNM system and grading are no longer sufficient, especially for individualized prognosis. Moreover, despite advances in treatment, studies have shown that the prognosis of patients with OSCC in terms of survival rate has not improved significantly, which is mainly due to the presence of treatment-resistant OSCC. Therefore, the identification of new, reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis and drug targets of OSCC is urgently needed. Meanwhile, the abundance of potential biomarkers for OSCC is difficult to keep track of. Therefore, the aim of the article was to provide an overview of articles listed in Pubmed® that deal with the topic of biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma, focusing in particular on the topic metabolism. Another question of this study was to set the focus on essential additive metabolic biomarkers, which can also be easily used in clinical routine.
Das orale Plattenepithelkarzinom (OSCC) ist einer der häufigsten bösartigen Tumoren weltweit mit steigender Inzidenz. Die chirurgische Behandlung ist anspruchsvoll und erfordert oft das gesamte Repertoire der plastischen Chirurgie.Diagnostisch sind nur wenige entscheidende Parameter relevant und noch weniger für eine individuelle und spezifische Medikamenten-Zielgruppenansprache. Um sehr komplexe chirurgische Prozesse auf ein akzeptables Maß anpassen zu können, ist eine individualisierte Prognoseberechnung unumgänglich.Leider reichen das klassische TNM-System und die Einstufung insbesondere für eine individualisierte Prognose nicht mehr aus. Darüber hinaus haben Studien trotz Fortschritten in der Behandlung gezeigt, dass sich die Prognose von Patienten mit oralen Plattenepithelkarzinom im Hinblick auf die Überlebensrate nicht wesentlich verbessert hat, was hauptsächlich auf das Vorhandensein von behandlungsresistentem oralen Plattenepithelkarzinomen zurückzuführen ist.Daher ist die Identifizierung neuer, zuverlässiger Biomarker für die Frühdiagnose und Wirkstoffziele von OSCC dringend erforderlich. Mittlerweile ist es schwierig, den Überblick über die Fülle an potenziellen Biomarkern für OSCC zu behalten.Ziel des Artikels war es daher, einen Überblick über in Pubmed® gelistete Artikel zu geben, die sich mit dem Thema Biomarker beim oralen Plattenepithelkarzinom beschäftigen und dabei insbesondere auf das Thema Stoffwechsel eingehen. Eine weitere Fragestellung dieser Studie bestand darin, den Fokus auf essenzielle additive metabolische Biomarker zu legen, die auch im klinischen Alltag problemlos eingesetzt werden können.
Keywords: OSCC; metabolic biomarker; prognosis; survival.
Copyright © 2025 Schreder et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




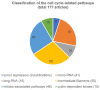

References
-
- Shen M, Shan W, Lv S, Cai K, Chen X, Xu Z, Gao M, Wang G. Risk factors for the occurrence of infection in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma after restorative reconstruction and its impact on recurrence and quality of life: a retrospective cohort study. Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Aug;12(8):2155–2168. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Panarese I, Aquino G, Ronchi A, Longo F, Montella M, Cozzolino I, Roccuzzo G, Colella G, Caraglia M, Franco R. Oral and Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic and predictive parameters in the etiopathogenetic route. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019 Feb;19(2):105–119. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1561288. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

