Tricuspid regurgitation and chronic kidney disease in patients with cardiogenic shock: Review of the literature and real-world experience from a single center
- PMID: 40535596
- PMCID: PMC12175724
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2025.101716
Tricuspid regurgitation and chronic kidney disease in patients with cardiogenic shock: Review of the literature and real-world experience from a single center
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) frequently complicates Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) and can worsen outcomes in cardiogenic shock. Tricuspid Regurgitation (TR), by elevating central venous pressure, may exacerbate renal impairment. Limited data exist regarding CKD's influence in TR interventions. This study assesses the impact of CKD on survival and explores RV dysfunction as a potential mediator in patients with TR in cardiogenic shock.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed patients admitted with HF-related or myocardial infarction-induced cardiogenic shock (2021-2025). Patients were stratified by TR severity (none/trivial, mild, moderate, severe) and CKD stage. Echocardiographic, laboratory, and hemodynamic data were collected. RV dysfunction was assessed using echocardiography and right heart catheterization. Survival outcomes, including HF readmissions and mortality, were evaluated using Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression, considering predictors significant at p < 0.10.
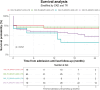
Results: Among 177 patients (median age 70 years, EF 35 %, 46 % Black), 55 % had CKD. TR severity distribution was: none/trivial 42 %, mild 16 %, moderate 22 %, and severe 20 %. Severe TR significantly increased in-hospital mortality (40 %) compared to non-severe TR (24 %) and correlated with worsening CKD stages. HF readmissions within 12 months occurred in 10 % of patients. Older age and RV dysfunction emerged as the strongest mortality predictors. Severe TR independently increased mortality and readmission risk.
Conclusion: Severe TR significantly worsens survival in cardiogenic shock patients, especially those with advanced CKD, mediated by RV dysfunction. CKD severity assessment may enhance patient stratification for valve interventions. Randomized studies are required to further validate these findings.
Keywords: Cardiogenic shock; Chronic kidney disease; Right ventricular failure; Tricuspid regurgitation.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Besler C., Orban M., Rommel K.P., Braun D., Patel M., Hagl C., Borger M., Nabauer M., Massberg S., Thiele H., Hausleiter J., Lurz P. Predictors of procedural and clinical outcomes in patients with symptomatic tricuspid regurgitation undergoing transcatheter edge-to-edge repair. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11(12):1119–1128. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2018.05.002. (PMID: 29929631) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nickenig G., Kowalski M., Hausleiter J., Braun D., Schofer J., Yzeiraj E., Rudolph V., Friedrichs K., Maisano F., Taramasso M., Fam N., Bianchi G., Bedogni F., Denti P., Alfieri O., Latib A., Colombo A., Hammerstingl C., Schueler R. Transcatheter treatment of severe tricuspid regurgitation with the edge-to-edge MitraClip technique. Circulation. 2017;135(19):1802–1814. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024848. (Epub 2017 Mar 23 PMID: 28336788) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous