Prospective study of continuous low-dose norepinephrine infusion during induction of anesthesia: effects on the stability of blood pressure and recovery quality in elderly patients undergoing robotic radical prostatectomy
- PMID: 40535617
- PMCID: PMC12170419
- DOI: 10.62347/HWWN6029
Prospective study of continuous low-dose norepinephrine infusion during induction of anesthesia: effects on the stability of blood pressure and recovery quality in elderly patients undergoing robotic radical prostatectomy
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of low-dose norepinephrine infusion on hemodynamic changes during anesthesia induction and its correlation with postoperative recovery in elderly patients undergoing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy.
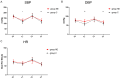
Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted on 63 elderly patients divided into two groups: the norepinephrine group (NE group) receiving 2-5 μg/kg·h norepinephrine by injection pump during anesthesia induction, and the control group (C group) with regular anesthesia. Heart rate (HR) and invasive blood pressure (BP) were recorded at four time points: before induction, pre-intubation lowest value (T1), post-intubation (T2), and lowest BP between intubation and skin incision (T3). Postoperative recovery (QoR-15) was evaluated on Days 1 and 3.
Results: Statistically significant differences in systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were observed between groups at T1 and T3 (P<0.05), but no significant differences in HR were found at any time point (P>0.05). The NE group had significantly higher SBP, DBP, and HR at T1 and T3 compared to the C group (P<0.05). Hemodynamic stability was significantly better in the NE group (P<0.05). No significant differences were seen in QoR-15 scores or postoperative hospital stay between groups (P>0.05), but the Barthel Index increased significantly in the NE group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Continuous low-dose norepinephrine infusion effectively reduced blood pressure and heart rate fluctuations during anesthesia induction. However, the study showed only a weak correlation between intraoperative hemodynamic changes and postoperative recovery.
Keywords: Hemodynamic stability; anesthesia induction; norepinephrine; postoperative recovery.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Partridge L, Deelen J, Slagboom PE. Facing up to the global challenges of ageing. Nature. 2018;561:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Murphy GS, Szokol JW, Greenberg SB, Avram MJ, Vender JS, Nisman M, Vaughn J. Preoperative dexamethasone enhances quality of recovery after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: effect on in-hospital and postdischarge recovery outcomes. Anesthesiology. 2011;114:882–890. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh R, Fard ZA. Renal effects of general anesthesia from old to recent studies. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:16944–16952. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
