Transurethral holmium laser enucleation of prostate shows remarkable efficacy in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 40535645
- PMCID: PMC12170422
- DOI: 10.62347/RKJN6285
Transurethral holmium laser enucleation of prostate shows remarkable efficacy in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of transurethral holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
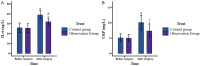
Methods: This retrospective study included 100 BPH patients who visited Foshan Fosun Chancheng Hospital from January 2022 to June 2023. Patients were divided into two groups: 50 treated with transurethral resection of the prostate (control group) and 50 with transurethral HoLEP (observation group). We compared clinical efficacy, surgical parameters, maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax), post-void residual volume (PRV), prostate-specific antigen (PSA), hemoglobin (Hb), interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), quality of life (QOL), and complication rates.
Results: The observation group showed significantly reduced operative time, blood loss, catheterization duration, and hospitalization compared to the control group (all P<0.05). Postoperatively, Qmax was higher and PRV lower in the observation group (both P<0.05). PSA was lower, and Hb was higher in the observation group than those in the control group (both P<0.05). Both IL-6 and CRP levels increased post-surgery, but were significantly lower in the observation group (both P<0.05). The observation group also had better IPSS and QOL scores and a lower complication rate (16% vs. 56%, all P<0.05).
Conclusion: HoLEP is an effective treatment for BPH, offering advantages such as reduced surgical time, lower complication rates, improved urodynamics, and better patient outcomes in terms of symptoms and quality of life.
Keywords: Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate; benign prostatic hyperplasia; efficacy; transurethral resection of the prostate.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and safety comparing greenlight laser vaporization with transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia with prostate volume less than 80 ml.Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Jun 8;38(1):133. doi: 10.1007/s10103-023-03794-2. Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37289405
-
Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus transurethral resection of the prostate: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Endourol. 2013 May;27(5):604-11. doi: 10.1089/end.2012.0505. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Endourol. 2013. PMID: 23167266
-
[Comparison of efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium fiber laser enucleation of prostate in patients with different prostate volumes].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Aug 18;57(4):711-716. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.013. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40754908 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Holmium laser ω-shaped pre-transection of prostate apex with preservation of the bladder neck improves urinary continence and sexual function in BPH patients after HoLEP].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2024 Dec;30(12):1091-1097. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2024. PMID: 40783919 Chinese.
-
Impact of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate on Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer in Patients With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms.Prostate. 2025 Aug;85(11):989-999. doi: 10.1002/pros.24906. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Prostate. 2025. PMID: 40275607
References
-
- Bertolo R, Dalpiaz O, Bozzini G, Cipriani C, Vittori M, Alber T, Maiorino F, Carilli M, Zeder R, Iacovelli V, Antonucci M, Sandri M, Bove P. Thulium laser enucleation of prostate versus laparoscopic trans-vesical simple prostatectomy in the treatment of large benign prostatic hyperplasia: head-to-head comparison. Int Braz J Urol. 2022;48:328–335. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abt D, Mullhaupt G, Hechelhammer L, Markart S, Gusewell S, Schmid HP, Mordasini L, Engeler DS. Prostatic artery embolisation versus transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: 2-yr outcomes of a randomised, open-label, single-centre trial. Eur Urol. 2021;80:34–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
