Luteolin alleviates Herpes Simplex Keratitis by inhibiting inflammatory responses via suppressing the PTGS2/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 40535652
- PMCID: PMC12170364
- DOI: 10.62347/IQUZ8416
Luteolin alleviates Herpes Simplex Keratitis by inhibiting inflammatory responses via suppressing the PTGS2/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Objective: Herpes Simplex Keratitis (HSK) is a leading cause of infectious-related blindness, primarily driven by corneal inflammation and dysregulated immune response. Luteolin (LUT), a flavonoid with anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties, has the potential to target key signaling pathways and provide therapeutic benefits. This study aimed to investigate the mechanisms through which LUT alleviates HSK.
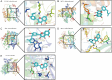
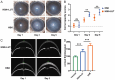
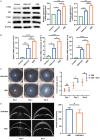
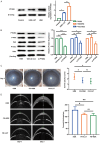
Methods: LUT's potential targets in HSK were identified using a systemic biology approach. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) analysis was performed to determine key hub genes. Molecular docking was used to assess LUT's binding affinity to PTGS2 and other key proteins. HSK mice were treated with LUT, and corneal opacity, edema, and thickness were then evaluated using slit-lamp microscopy and Optical Coherence Tomography. Inflammatory cytokine levels were quantified by quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR (qRT-PCR), while PTGS2/NF-κB pathway activation, PTGS2 expression, and NF-κB phosphorylation levels were assessed by Western Blotting (WB).
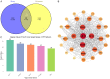
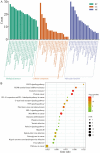
Results: LUT was found to regulate 30 HSK-related proteins, with AKT1, TNF, and PTGS2/NF-κB identified as key nodes. Furthermore, molecular docking confirmed a strong binding to PTGS2 (-9.7 kcal/mol). LUT treatment significantly reduced corneal opacity and edema, restoring corneal thickness to near-normal levels. RT-qPCR revealed downregulation of inflammatory cytokines, and WB analysis showed decreased PTGS2 expression and NF-κB phosphorylation, confirming LUT's role in attenuating corneal inflammation via inhibiting the PTGS2/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Conclusions: LUT alleviates HSK by modulating the PTGS2/NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing inflammation and corneal damage, and highlighting its therapeutic potential for ocular inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Herpes Simplex Keratitis; LUT; PTGS2/NF-κB; Traditional Chinese Medicine; inflammatory response.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Harris KD. Herpes Simplex Virus Keratitis. Home Healthc Now. 2019;37:281–284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
