Effects of metformin combined with insulin aspart on gestational weight gain, lipid metabolism, immune function, and delivery outcomes in pregnant women with gestational diabetes
- PMID: 40535659
- PMCID: PMC12170393
- DOI: 10.62347/ROSD8026
Effects of metformin combined with insulin aspart on gestational weight gain, lipid metabolism, immune function, and delivery outcomes in pregnant women with gestational diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of metformin combined with insulin aspart on gestational weight gain, lipid metabolism, immune function, and delivery outcomes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
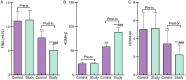
Methods: Clinical data from 95 GDM patients were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were divided into two groups: the control group (45 cases) received only insulin aspart, and the study group (50 cases) received a combination of metformin and insulin aspart. Clinical efficacy, blood glucose levels, body weight, lipid metabolism levels [total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low - density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)], immune function, insulin resistance [fasting insulin (FINS), homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)], inflammatory markers, delivery outcomes, and drug safety were compared between the two groups.
Results: The study group had a significantly higher total effective rate (96.00%) compared to the control group (80.00%) (P < 0.05). Post-treatment, blood glucose levels decreased significantly in both groups, with lower levels observed in the study group (all P < 0.05). Both groups showed weight gain, but the increase was less in the study group (P < 0.05). Levels of TC, TG, LDL-C, FINS, HOMA-IR, and inflammatory markers decreased significantly in both groups, with greater reductions in the study group (all P < 0.05). HDL-C, immune function markers, and HOMA-β increased, with more significant increases in the study group (all P < 0.05). The incidence of adverse delivery outcomes was significantly lower in the study group (26.00% vs. 62.22%) (P < 0.05), with no significant difference in adverse reaction rates (10.00% vs. 8.89%) (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Metformin combined with insulin aspart demonstrates significant therapeutic benefits in treating GDM. It effectively regulates blood glucose and lipid metabolism, controls weight gain, enhances immune function, reduces insulin resistance, suppresses inflammation, and lowers the incidence of adverse delivery outcomes, with good drug safety.
Keywords: Gestational diabetes mellitus; delivery outcomes; immune function; insulin aspart; lipid metabolism; metformin; weight.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of insulin aspart combined with insulin detemir and metformin on islet function in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Drug Target. 2025 Sep;33(8):1394-1398. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2025.2477074. Epub 2025 Apr 2. J Drug Target. 2025. PMID: 40049655 Clinical Trial.
-
Elevated TXNIP and reduced PINK1 in gestational diabetes mellitus: association with dyslipidemia and pregnancy complications.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):4986-4995. doi: 10.62347/BUUI5663. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40821039 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Effects of vitamin D supplementation on glucose metabolism, lipid concentrations, inflammation, and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial.Am J Clin Nutr. 2013 Dec;98(6):1425-32. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.072785. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013. Retraction in: Am J Clin Nutr. 2021 May 8;113(5):1382. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab071. PMID: 24132976 Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of acupuncture and moxibustion therapy on glycolipid metabolism in patients with obese-type polycystic ovarian syndrome: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 13;104(24):e42812. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042812. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40527787 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vince K, Perković P, Matijević R. What is known and what remains unresolved regarding gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) J Perinat Med. 2020;48:757–763. - PubMed
-
- Tsakiridis I, Giouleka S, Mamopoulos A, Kourtis A, Athanasiadis A, Filopoulou D, Dagklis T. Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus: an overview of national and international guidelines. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2021;76:367–381. - PubMed
-
- Chatzakis C, Cavoretto P, Sotiriadis A. Gestational diabetes mellitus pharmacological prevention and treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27:3833–3840. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
