Local injection of platelet-rich plasma is effective for non-healing hand wounds
- PMID: 40535666
- PMCID: PMC12170399
- DOI: 10.62347/CRQK7620
Local injection of platelet-rich plasma is effective for non-healing hand wounds
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the clinical efficacy of local platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections in treating non-healing hand wounds.
Methods: Data of 80 patients with non-healing hand wounds were retrospectively selected for this study. Among them, 48 patients in the research group received local PRP injections, while 32 patients in the control group were treated with conventional dressing changes. The outcomes assessed included treatment efficacy, safety, frequency of dressing change, wound healing time, duration of hospitalization, treatment costs, wound healing rate, wound infection rate, Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) scores, Bates-Jensen Wound Assessment Tool (BWAT) scores, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores, serum wound growth factors, and patient satisfaction with wound appearance.
Results: The research group demonstrated significantly superior outcomes compared to the control group, including higher overall treatment efficacy and wound healing rates. Furthermore, the research group exhibited a significantly lower incidence of adverse events, reduced frequency of dressing changes, shorter wound healing time, reduced hospitalization duration, lower treatment costs, and a lower infection rate. Post-treatment assessments revealed significantly lower VSS, BWAT, and VAS scores in the research group. Additionally, the upregulation of serum wound growth factors was more pronounced in the research group following treatment.
Conclusions: Local PRP injection demonstrates clear efficacy in the management of non-healing hand wounds.
Keywords: Platelet-rich plasma; clinical efficacy; local injection; non-healing hand wounds.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
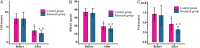

References
-
- Singh S, Aggarwal AK, Gudisa R, Batra P, Rathi NK, Madan V, Thakur V, Sharma H, Kumar R, Khare S, Singhal L, Chaudhry R, Arora N, Singh H, Kaur J, Sharma A, Dakhale GN, Sharma V, Gautam V. A novel potential treatment for diabetic foot ulcers and non-healing ulcers - case series. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Pena OA, Martin P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25:599–616. - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum SR, Carter MJ, Fife CE, DaVanzo J, Haught R, Nusgart M, Cartwright D. An economic evaluation of the impact, cost, and medicare policy implications of chronic nonhealing wounds. Value Health. 2018;21:27–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
