Augmentation laryngoplasty: Results and decision plan
- PMID: 40535740
- PMCID: PMC12172133
- DOI: 10.1002/wjo2.212
Augmentation laryngoplasty: Results and decision plan
Abstract
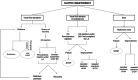
Objectives: Augmentation laryngoplasty represents a therapeutic choice for patients who suffer from glottic insufficiency of different etiologies. There have been multiple injectables that have been proven effective. The present study examines the short-term effects of vocal fold augmentation on phonation, swallowing, and breathing in individuals with glottic insufficiency. In addition, a decision plan is also proposed.
Methods: Data from medical records and operative notes were used to conduct a retrospective cohort study on patients with glottic insufficiency who underwent vocal fold augmentation from 2016 to 2023. Hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxyapatite, and polydimethylsiloxane were the injectable materials that were used. An analysis was conducted on phonation, breathing, swallowing, and laryngoscopy findings both before and after vocal folds' augmentation.
Results: Seventy-nine patients were included, which represents 97 injections. The median (IQR) preoperative Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10) score improved from 21 (15-28) to 16 (9-25) postoperatively (p < 0.001). The GRBAS scale also significantly decreased (p < 0.001). The median (IQR) preoperative Dyspnea Index score improved from 6 (0-17) to 2 (0-10) postoperatively (p < 0.05). Laryngoscopic findings showed significant improvement in the bulk of the vocal folds. There was no significant change in swallowing.
Conclusions: In case of dysphonia secondary to glottic insufficiency, augmentation laryngoplasty using various injectable materials has proven to be an effective option across a range of different etiologies, as it results in significant improvements in voice quality. The choice of the injectable material depends upon the severity and the etiology of glottic insufficiency.
Keywords: augmentation laryngoplasty; glottic insufficiency; presbylarynx; vocal fold augmentation; vocal fold paralysis; vocal fold scar.
© 2024 The Author(s). World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd on behalf of Chinese Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Injection laryngoplasty with hyaluronic acid for glottal insufficiency in unilateral vocal fold paralysis: a systematic review of the literature.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Nov;279(11):5071-5079. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07437-0. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35767054
-
Diagnostic Vocal Fold Augmentation in Patients With Both Age-related Vocal Fold Atrophy and Parkinson's Disease.J Voice. 2025 Aug 20:S0892-1997(25)00301-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2025.07.039. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 40841198
-
Treatment Durability of Injection Augmentation of Vocal Fold Atrophy.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2025 Aug 6;10(4):e70223. doi: 10.1002/lio2.70223. eCollection 2025 Aug. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40771842 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Voice and Swallowing: A Cross-Sectional Study on Percutaneous Injection Medialisation Laryngoplasty Outcomes in Patients of Unilateral Vocal Cord Palsy.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Mar;77(3):1410-1417. doi: 10.1007/s12070-025-05352-4. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40093433
-
Efficacy of Injectable Laryngoplasty With Hyaluronic Acid and/or Calcium Hydroxyapatite in the Treatment of Glottic Incompetence. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Voice. 2025 Jul;39(4):945-953. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.01.020. Epub 2023 Feb 17. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 36804345 Review.
References
-
- Onwordi LN, Al Yaghchi C. Airway glottic insufficiency. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30855795 - PubMed
-
- Rosen CA, Gartner‐Schmidt J, Casiano R, et al. Vocal fold augmentation with calcium hydroxylapatite: twelve‐month report. Laryngoscope. 2009;119:1033‐1041. - PubMed
-
- Rudolf R, Sibylle B. Laryngoplasty with hyaluronic acid in patients with unilateral vocal fold paralysis. J Voice. 2012;26:785‐791. - PubMed
-
- Sulica L, Rosen CA, Postma GN, et al. Current practice in injection augmentation of the vocal folds: indications, treatment principles, techniques, and complications. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:319‐325. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
