Hypoxia regulates glycolysis through the HIF-1α/BMAL1/ALDOC axis to reduce oxaliplatin sensitivity in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 40535800
- PMCID: PMC12171004
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.108582
Hypoxia regulates glycolysis through the HIF-1α/BMAL1/ALDOC axis to reduce oxaliplatin sensitivity in colorectal cancer
Abstract
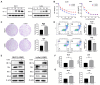
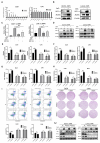
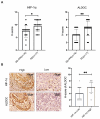
Background: Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is a first-line chemotherapy agent for advanced colorectal cancer (CRC), but the development of resistance often compromises its efficacy. Tumor hypoxia and metabolic reprogramming are known to influence chemotherapy sensitivity, yet their interrelationship remains inadequately explored. Methods: In vitro assays were conducted using human colorectal cancer cell lines (DLD1 and LoVo) under hypoxic conditions induced by cobalt chloride (CoCl2). The expression levels of key proteins involved in the HIF-1α/BMAL1/ALDOC pathway were assessed through Western blotting and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Cell viability, apoptosis, and glycolytic activity were evaluated using CCK-8 assays, flow cytometry, and lactate/ATP measurements. Results: Hypoxia significantly enhanced glycolysis in CRC cells, decreasing sensitivity to L-OHP. The HIF-1α/BMAL1/ALDOC axis was identified as a crucial mediator in this process, with HIF-1α upregulating BMAL1, which increased ALDOC expression. This cascade promoted glycolytic activity and reduced apoptosis in hypoxic conditions. Notably, a positive correlation between HIF-1α and ALDOC expression was confirmed in clinical CRC samples. Conclusion: The findings reveal a novel mechanism by which hypoxia diminishes L-OHP sensitivity in CRC through the HIF-1α/BMAL1/ALDOC pathway. These insights provide potential biomarkers for predicting treatment outcomes and suggest new therapeutic strategies to enhance chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer.
Keywords: ALDOC; HIF-1α; chemotherapy; glycolysis; hypoxia.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KunMingShanHaiTang formula reprograms macrophage metabolism and promotes M2 polarization via the HIF-1α pathway to alleviate ulcerative colitis symptoms in a rat model.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2025 Jun;57(2-3):119-145. doi: 10.1007/s10863-025-10056-z. Epub 2025 Apr 2. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2025. PMID: 40172736 Free PMC article.
-
Purple Potato Extract Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Metabolic Reprogramming and Inhibits HIF-1α Signaling in Caco-2 Cells.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 23;17(13):2079. doi: 10.3390/nu17132079. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647184 Free PMC article.
-
Zeaxanthin improves myopia by regulating the HIF-1α-glycolysis signaling pathway.Exp Eye Res. 2025 Oct;259:110557. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2025.110557. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Exp Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40738388
-
The Roles and Molecular Mechanisms of HIF-1α in Pulpitis.J Dent Res. 2025 Jul;104(7):715-724. doi: 10.1177/00220345251320970. Epub 2025 Mar 18. J Dent Res. 2025. PMID: 40102725 Review.
-
Advances in the mechanisms of HIF-1α-enhanced tumor glycolysis and its relation to dedifferentiation.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2025 Sep;197:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2025.05.003. Epub 2025 May 13. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40373959 Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Racker E. Bioenergetics and the problem of tumor growth. American scientist. 1972;60:56–63. - PubMed
-
- Guzy RD, Hoyos B, Robin E, Chen H, Liu L, Mansfield KD. et al. Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and cellular oxygen sensing. Cell metabolism. 2005;1:401–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

