Navigating the role of protein lactylation in prostate cancer and its implications for immunotherapy
- PMID: 40535811
- PMCID: PMC12171000
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.114137
Navigating the role of protein lactylation in prostate cancer and its implications for immunotherapy
Abstract
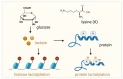
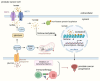
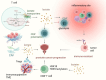
Prostate cancer is an aggressive malignancy with high prevalence and significant mortality, characterized by its remarkable metabolic adaptability and immune complexity. Emerging evidence has highlighted the critical role of post-translational modifications (PTMs) in cancer biology, with protein lactylation gaining attention as a novel PTM with profound implications. Lactylation, derived from lactate, links the altered metabolic processes of tumor cells to diverse cellular functions, including epigenetic regulation and protein dynamics. It significantly influences tumor progression, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance by modulating key immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. The immunosuppressive conditions created by lactate and lactylation favor tumor survival in prostate cancer. Thus, targeting lactylation offers innovative strategies for treating prostate cancer. By leveraging lactylation modulation, particularly in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors, there is potential to enhance anti-tumor immune responses and improve treatment outcomes. This review explores the intersection of metabolic alterations and immune modulation, underscoring lactylation as a promising therapeutic avenue in prostate cancer.
Keywords: immune checkpoints; immunotherapy; lactylation; prostate cancer; tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring lactylation and cancer biology: insights from pathogenesis to clinical applications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 13;13:1598232. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1598232. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40584966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactylation-mediated miRNA regulation in cancer therapy resistance.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 19;23(1):941. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06959-5. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40830798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactate and lactylation: emerging roles in autoimmune diseases and metabolic reprogramming.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1589853. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589853. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40655145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding the lactylation landscape: Implications for tumor microenvironment remodeling and marine algal saccharide-based therapeutic interventions.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug 13;147:157169. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157169. Online ahead of print. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40834612
-
Lactylation: A new direction for tumor-targeted therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Jul 30;1880(5):189399. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2025.189399. Online ahead of print. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40750087 Review.
References
-
- Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Van den Broeck T, Brunckhorst O, Darraugh J. et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2024 Update. Part I: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur Urol. 2024;86:148–63. - PubMed
-
- Cai M, Song XL, Li XA, Chen M, Guo J, Yang DH. et al. Current therapy and drug resistance in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 2023;68:100962. - PubMed
-
- Buck SAJ, Koolen SLW, Mathijssen RHJ, de Wit R, van Soest RJ. Cross-resistance and drug sequence in prostate cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 2021;56:100761. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

