Two-Sample Network Mendelian Randomization and Single-Cell Analysis Reveal the Causal Associations and Underlying Mechanisms Between Antihypertensive Drugs and Kidney Cancer
- PMID: 40535814
- PMCID: PMC12170992
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.110850
Two-Sample Network Mendelian Randomization and Single-Cell Analysis Reveal the Causal Associations and Underlying Mechanisms Between Antihypertensive Drugs and Kidney Cancer
Abstract
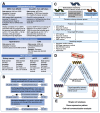
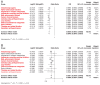
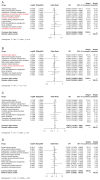
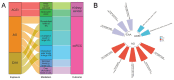
Background: Antihypertensive drugs represent the most widely used drugs worldwide. However, the association between antihypertensive drugs and the risk of kidney cancer remains unclear. This study innovatively integrates multi-omics and causal inference approaches to investigate the long-term effects and potential mechanisms of 12 antihypertensive drug classes on kidney cancer risk. Methods: In this study, novel approaches including two-sample mendelian randomization (MR), summary-data-based mendelian randomization (SMR), two-step network MR, and single-cell transcriptomic analysis were employed. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were obtained from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) to proxy exposures and outcomes. The cis-expression quantitative trait loci (cis-eQTL) as the proxies of exposure were also obtained. MR estimates were generated using the inverse-variance weighted method or Wald ratio method. Sensitivity analyses were undertaken to interrogate the robustness of the main findings. Two-step network MR and single-cell analysis were specifically designed to dissect pathway-level mediation and expression patterns of identified targets. Results: In the main analysis, genetically proxied calcium-channel blockers (odds ratio [OR]: 0.95, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.91-0.99, p=0.021) and vasodilator antihypertensives (OR: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.76-0.97, p=0.018) were suggestively associated with decreased risk of kidney cancer, whereas genetically proxied angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (OR: 1.13, 95% CI: 1.00-1.27, p=0.043) was suggestively associated with increased risk of kidney cancer. Genetically proxied antiadrenergic agents (OR=0.94, 95% CI: 0.90-0.99, p=0.021) and centrally acting antihypertensives (OR=0.93, 95% CI: 0.88-0.98, p=0.010) were suggestively associated with a decreased risk of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. SMR analysis revealed that these suggestively significant associations might be driven by CACNA1C, CALM1, ACE, and LTA4H. Upon two-step network MR analyses, 10 pathways with directional consistency were identified, and the mediation proportion ranged from 3.22% to 7.12%. The influence of antihypertensive drugs on kidney cancer risk might be associated with their regulation of levels of blood cells and lipids. Single-cell analysis further revealed the expression patterns of the four identified targets in peripheral blood and tumor infiltrating immune cells. Conclusion: This study pioneers the integration of causal inference and single-cell omics to demonstrate that antihypertensive drugs modulate kidney cancer risk through target-specific mechanisms involving blood cell and lipid pathways. Our findings provide actionable targets (CACNA1C, CALM1, ACE, and LTA4H) for drug repurposing trials and underscore the clinical importance of personalized antihypertensive therapy in cancer prevention.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; antihypertensive drugs; drug target; kidney cancer; single-cell analysis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Schafer EJ, Jemal A, Wiese D. et al. Disparities and Trends in Genitourinary Cancer Incidence and Mortality in the USA. Eur Urol. 2023;84:117–26. - PubMed
-
- Bukavina L, Bensalah K, Bray F. et al. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma: 2022 Update. Eur Urol. 2022;82:529–42. - PubMed
-
- Moch H, Amin MB, Berney DM. et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur Urol. 2022;82:458–68. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Leung DK-W, Chan EO-T. et al. A Global Trend Analysis of Kidney Cancer Incidence and Mortality and Their Associations with Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and Metabolic Syndrome. Eur Urol Focus. 2022;8:200–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

