High MIG-6 expression promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer
- PMID: 40535815
- PMCID: PMC12170504
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.98431
High MIG-6 expression promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer
Abstract
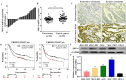
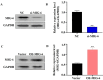
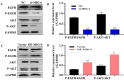
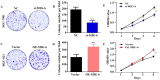
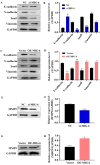
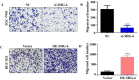
Background: Mitogen-inducible gene-6 (MIG-6) is a feedback inhibitor that targets activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and suppresses tumor growth fueled by constitutively activated EGFR. Nevertheless, the action mechanism of MIG-6 in gastric cancer (GC) remains to be elucidated. Methods: Western blotting, fluorescence quantitative PCR, and immunohistochemistry were performed to detect the expression of MIG-6 in GC cell lines and tissues. Public databases were used to analyze MIG-6 in patients with GC. Furthermore, the GC cell lines were selected for the knockdown and overexpression of MIG-6. Results: Bioinformatics and histological analyses showed that MIG-6 was elevated in human GC tissues and cells. The Kaplan-Meier plotter showed that patients with elevated MIG-6 expression had significantly shorter survival. Furthermore, small interference RNA-mediated reduction of MIG-6 expression decreased EGFR/AKT signaling, as well as the proliferation and metastasis of human GC cells in vitro, whereas its overexpression increased these actions. Also, MIG-6 overexpression promoted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of GC cells as well as the expression of the migration-associated protein matrix metalloproteinase-9 in vitro. Conclusion: These results suggest that MIG-6 can serve as a new prognostic biomarker or potential therapeutic target for the identification of patients with poor survival.
Keywords: EGFR; Gastric cancer; MIG-6; metastasis; proliferation; survival..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RGS4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through the focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 14;31(2):100898. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39811500 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine kinase 1 facilitates gastric cancer progression via STAT1 gene methylation-mediated mechanisms.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):3226-3238. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-948. Epub 2025 May 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530131 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis reveals NTN1 as an immune infiltrate risk factor and its potential prognostic value in SKCM.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85444-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863609 Free PMC article.
-
Olaparib Monotherapy or in Combination with Abiraterone for the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) and a BRCA Mutation.Target Oncol. 2025 May;20(3):445-466. doi: 10.1007/s11523-025-01146-4. Epub 2025 May 21. Target Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40397306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2020;396:635–48. - PubMed
-
- Lordick F, Carneiro F, Cascinu S, Fleitas T, Haustermans K, Piessen G. et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2022;33:1005–20. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Chen C, Ding Q, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Chen J. et al. METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut. 2020;69:1193–205. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

